In hazardous environments, one mistake can put workers at serious risk. Many companies, especially in chemical manufacturing, oil and gas, and emergency response, face constant concerns about toxic gases and chemical exposure. Buyers like you may often struggle with questions: Which protective suits truly guarantee safety? How do you know if a supplier is meeting the highest global standards? This is where NFPA 1991 certification becomes the gold standard for hazmat suits.
NFPA 1991 is critical because it ensures gas-tight protection, meaning suits are tested and proven to resist dangerous chemicals, vapors, and gases under extreme conditions. This standard not only saves lives but also prevents costly operational failures and liability issues.
Therefore, when we look deeper, NFPA 1991 is not just a technical requirement. It is a symbol of trust. For buyers in America, Europe, and beyond, choosing NFPA 1991-certified hazmat suits removes uncertainty. It gives your team the confidence to enter hazardous environments knowing the gear will not fail.
What Does NFPA 1991 Certification Cover?
NFPA 1991 certification sets the benchmark for protective ensembles designed for chemical, biological, and industrial hazardous environments. It specifies performance requirements for fully encapsulating, gas-tight hazmat suits. Because hazardous vapors spread faster than liquids, the standard ensures suits are designed to withstand the most dangerous forms of exposure.
NFPA 1991 defines critical aspects like suit material resistance, gas-tight zippers, seam strength, visor durability, and pressure testing. It ensures that hazmat suits are capable of protecting against direct chemical exposure, pressurized leaks, and high concentrations of toxic vapors.
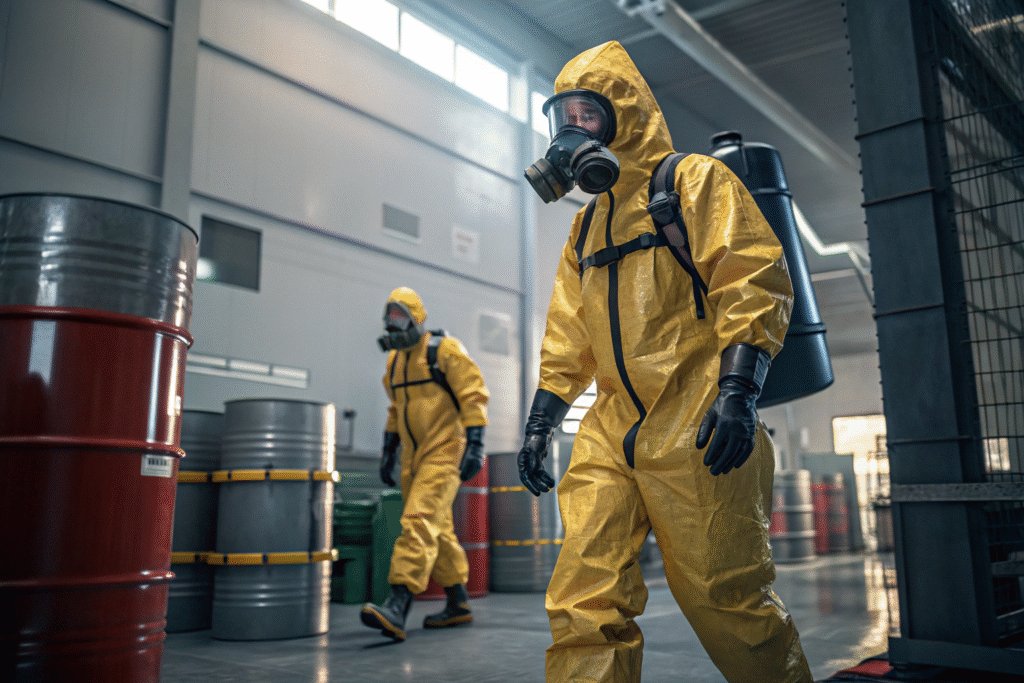

How Does NFPA 1991 Testing Work?
Testing involves placing the suit under rigorous conditions, including inflation testing for leaks, exposure to toxic chemicals, and performance under pressure. For instance, materials are evaluated for permeation resistance against industrial chemicals like ammonia and chlorine. You can see detailed test methods in OSHA’s hazmat suit guidance and NFPA’s official documentation.
Why Is Gas Tightness the Priority?
Gas-tight suits are essential because many dangerous substances exist in vapor form, which penetrates faster than liquids. Unlike splash suits, NFPA 1991-certified gear prevents vapor infiltration, which is vital during chemical spills, tanker accidents, or industrial fires. You can compare gas-tight vs. splash protection in this CDC resource.
In summary, by setting such rigorous benchmarks, NFPA 1991 ensures that every certified suit is reliable in extreme conditions, and this reliability directly builds buyer confidence.
How Does NFPA 1991 Protect Against Toxic Vapors?
The main purpose of NFPA 1991 is to stop hazardous gases from entering the suit. A small failure in sealing can lead to dangerous inhalation, so strict airtightness is non-negotiable.
The standard requires suits to pass “pressure decay tests,” proving that zippers, visors, gloves, and seams remain airtight under stress. This level of testing simulates real-world emergency leaks.
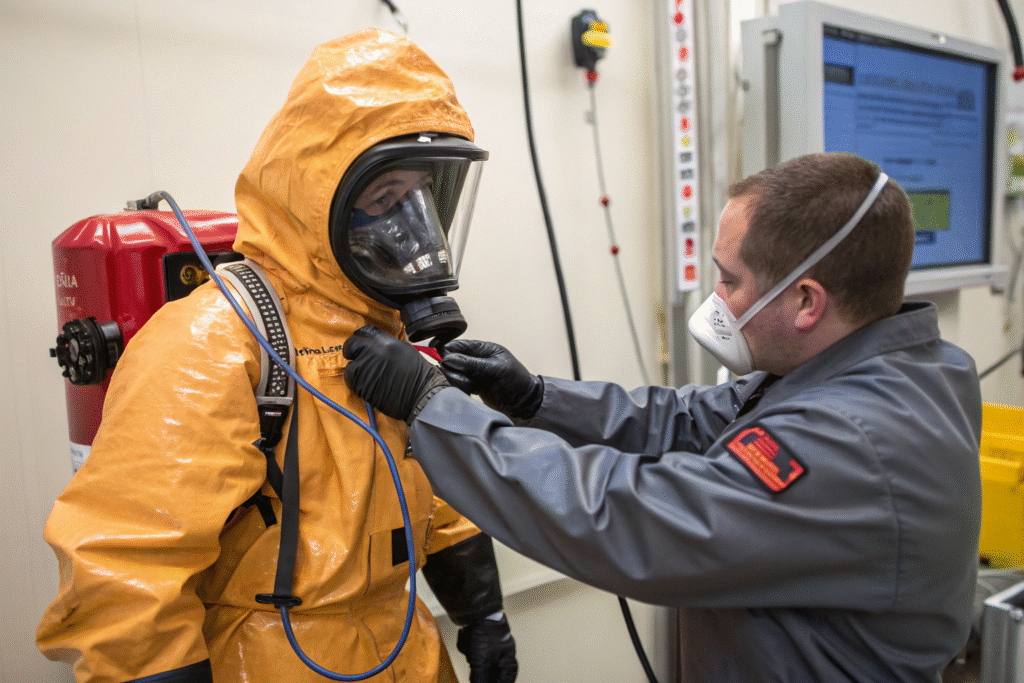

What Are Common Hazards NFPA 1991 Suits Defend Against?
They protect against chemicals like hydrogen sulfide, chlorine, ammonia, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). For reference, the EPA’s hazardous air pollutants list includes many of these dangerous gases.
What Happens Without Gas Tightness?
If a suit is not gas-tight, vapors can bypass the protective layer. This means respiratory systems are compromised, even when workers use air supply systems. That’s why both NFPA 1991 and NIOSH respirator standards are often combined in hazmat protocols.
As a result, NFPA 1991 does not just focus on protection—it ensures survival in scenarios where a fraction of a second or a minor leak could decide life or death.
What Are the Buyer’s Risks Without NFPA 1991?
As a buyer, ignoring NFPA 1991 can lead to multiple risks. Over time, non-certified suits increase the likelihood of accidents, penalties, and supply chain disruptions.
Without NFPA 1991 certification, there is no guarantee that the suit can withstand toxic gas infiltration. This increases the risk of worker injury, lawsuits, regulatory fines, and loss of trust from clients.
Why Should American Buyers Insist on NFPA 1991?
In the U.S., OSHA regulations often reference NFPA standards for compliance. Choosing uncertified suits can result in non-compliance penalties. See OSHA’s PPE compliance guide.
How Do Delays and Tariffs Add to the Problem?
For buyers importing from Asia, logistical issues, sailing schedules, and tariffs already add complexity. NFPA 1991-certified suits reduce risk by ensuring fewer shipment rejections and smoother customs clearance. Trade guidance on this is explained in U.S. Customs import rules.
Consequently, NFPA 1991 helps global buyers cut uncertainty, streamline procurement, and secure long-term operational safety.
Why Choose a Supplier with NFPA 1991 Expertise?
Partnering with a supplier who understands NFPA 1991 saves time and money. At Fumao, we integrate fabric testing, coating, seam sealing, and packaging under one system, so every step follows international safety requirements.
We help buyers by providing NFPA-aligned fabric solutions, reducing development cycles, and ensuring compliance with U.S. and EU import regulations.
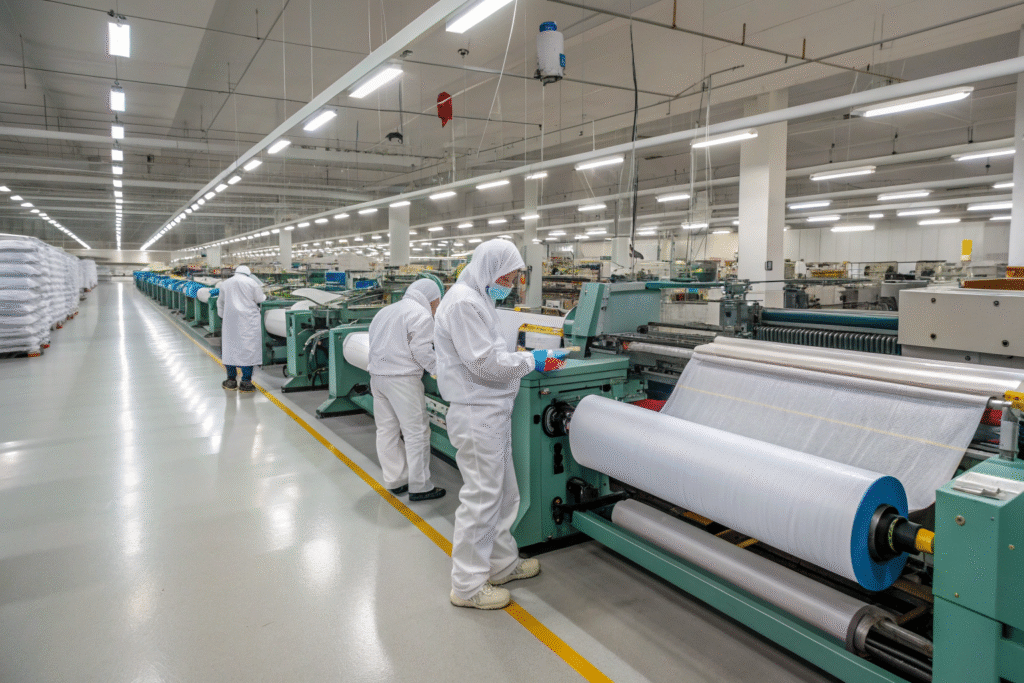

What Makes Fumao a Strong Partner?
We operate weaving, dyeing, printing, coating, and packaging factories, plus a CNAS-certified lab. Buyers gain the benefit of 48-hour sample development and AI-driven fabric innovation. You can learn more about sustainable textiles on Textile Exchange.
How Do We Simplify Global Delivery?
With supply hubs in Keqiao and overseas warehousing, we provide fast customs clearance and multimodal logistics. Our experience with EU, U.S., and Belt & Road markets ensures your shipments arrive on time. Insights into textile trade routes are explained on World Trade Organization.
Therefore, choosing Fumao means gaining a partner who not only supplies fabrics but also ensures compliance, efficiency, and peace of mind.
Recraft指令--A panoramic view of a modern textile factory floor with advanced weaving and coating machines producing hazmat fabrics, workers in safety uniforms, bright lighting, industrial realism, accurate machinery and clear human expressions.
Conclusion
NFPA 1991 is not just a technical requirement. It is a safeguard for workers, a compliance guarantee for companies, and a reassurance for buyers. Choosing gas-tight hazmat suits that meet this standard protects against toxic gas infiltration, prevents costly failures, and ensures smooth operations across borders.
If you are sourcing protective fabrics or hazmat suit materials, we at Shanghai Fumao can provide NFPA-aligned, high-performance textiles. To discuss custom orders or compliance solutions, you can contact our Business Director, Elaine at elaine@fumaoclothing.com.










