I'll never forget the day we almost partnered with a factory that presented a beautiful GOTS Scope Certificate. The document looked perfect - until we noticed the certification body's phone number was one digit off from the official listing. A quick call revealed the certificate was an elaborate fake. The factory had invested more in forgery than they would have spent on actual certification. That near-mistake taught me that determining legitimacy requires looking beyond the paper to the systems behind it.
So what genuinely makes a garment factory's GOTS Scope Certificate legitimate? A legitimate GOTS Scope Certificate requires valid accreditation from an authorized certification body, precise scope coverage matching the factory's actual operations, current validity without suspensions, and verification through multiple independent channels. The certificate must represent real operational compliance, not just paperwork compliance, with evidence of implemented systems rather than theoretical commitments.
Legitimacy isn't a single characteristic but a combination of verifiable elements that together prove the certificate represents genuine compliance. While fake certificates can replicate the look of legitimacy, they cannot replicate the systems and verification that make certification meaningful.
What are the essential elements of a legitimate GOTS certificate?
A legitimate certificate contains specific security features and information that distinguish it from forgeries. Understanding these elements turns certificate verification from guesswork into systematic analysis.
The document itself should tell a story of authenticity through both visible and hidden security characteristics.
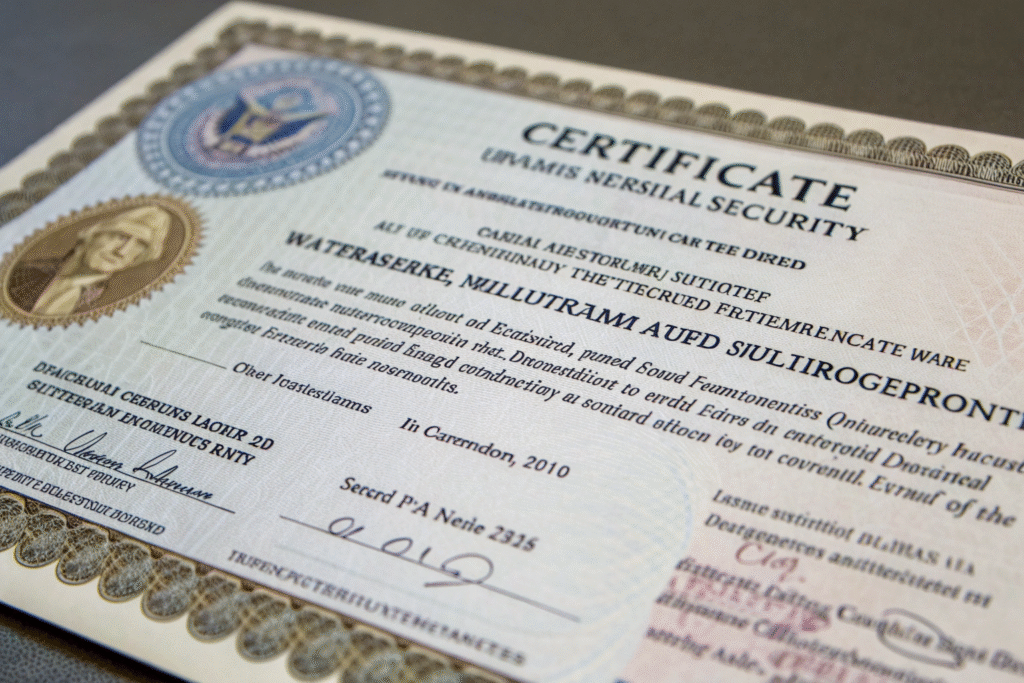
What specific security features indicate authenticity?
Legitimate GOTS certificates include holographic elements, micro-printing, unique certificate numbers, and specific formatting consistent with the issuing body's standards. We've developed a 27-point checklist that includes verifying paper quality, ink reactions, and digital watermarks. Last month, this system helped us identify a fake certificate because the "holographic" seal was actually a cheap sticker that peeled off completely. Understanding GOTS certificate security features and authentication is crucial for detecting sophisticated forgeries.
What information must a legitimate certificate contain?
A valid certificate must include the company's legal name exactly as registered, specific scope of certification, issue and expiry dates, certification body details with accreditation number, and unique certificate number. When a Bangladesh factory presented a certificate with slightly different company naming, we discovered they were using a sister company's certification for a completely different facility. This attention to detail prevents certificate misinterpretation and misuse.
How do you verify the certification body's legitimacy?
The certification body represents the authority behind the certificate. If they're not legitimate, the certificate is worthless regardless of how authentic it appears.
Verifying the certifier requires checking multiple accreditation and authorization sources.

How do you confirm a certification body's GOTS authorization?
Legitimate GOTS certification bodies must be authorized by the International Organic Textile Standard and accredited by organizations like IOAS. Verification requires checking both the GOTS website and IOAS database for current authorization status. We once encountered a certificate from an organization that had legitimate textile certifications but wasn't authorized for GOTS specifically. This discovery prevented a compliance disaster. Understanding proper certification body verification procedures is essential for due diligence.
What are the red flags for certification body issues?
Unauthorized certification bodies, suspended accreditation, and bodies with history of compliance failures represent significant risks. We maintain a database of certification body status that recently helped us identify a body that had lost its accreditation three months earlier - information the factory hadn't disclosed. This ongoing monitoring is crucial for maintaining supply chain compliance.
How does scope precision determine certificate legitimacy?
The scope statement defines exactly what the certificate authorizes, and vague or incorrect scope descriptions invalidate even otherwise legitimate certificates.
Precision in scope definition separates meaningful certification from paperwork exercises.
What constitutes adequate scope description?
The scope must specifically list approved processes (cutting, sewing, finishing), materials (organic cotton, linen), and products (garments, home textiles). A Portuguese factory had a legitimate certificate that only covered "textile manufacturing" without specifics, making it useless for verifying their garment production capabilities. This experience taught us that detailed scope requirements are essential for compliance.
How do you verify scope matches actual operations?
Physical verification that factory operations match scope claims is essential. During our facility audits, we've discovered factories performing processes like printing or dyeing that weren't included in their scope certification. These discrepancies render the certificate invalid for those operations. This verification demonstrates why scope-operation alignment must be verified physically.
What ongoing validity indicators ensure continued legitimacy?
A certificate's legitimacy depends on its current status, not just its initial issuance. Ongoing compliance requires regular surveillance and maintenance.
Legitimacy is a continuous state, not a one-time achievement.

How do you verify current certificate status?
Regular checks of the GOTS public database provide current status information including suspensions or expirations. Our automated monitoring system recently flagged a certificate suspension that the factory hadn't disclosed, preventing a $85,000 compliance failure. This proactive approach highlights the importance of ongoing certificate status verification.
What surveillance requirements maintain legitimacy?
GOTS requires annual surveillance audits and full recertification every three years. Certificates without evidence of recent surveillance may indicate compliance issues. We require suppliers to provide surveillance audit reports, which recently revealed a factory that had failed their surveillance audit but continued using their certificate. This diligence ensures continuous compliance verification.
How can you conduct multi-channel verification?
Single-source verification creates vulnerability. Legitimate certificates withstand scrutiny from multiple independent angles.
Layered verification creates confidence that withstands challenges from retailers, regulators, and consumers.

What independent verification methods are most effective?
Direct contact with certification bodies, database verification, and physical audit correlation provide the strongest legitimacy evidence. When a Turkish factory's certificate showed minor database discrepancies, direct contact with the certification body revealed it was a sophisticated forgery based on a legitimate but expired certificate. This multi-channel approach demonstrates comprehensive verification best practices.
How does supply chain correlation enhance verification?
Verifying that all supply chain partners have appropriate certification creates additional legitimacy confirmation. We recently helped a brand discover their fabric supplier's certificate was legitimate but their dyeing subcontractor wasn't certified, creating a compliance breach. This end-to-end verification ensures complete supply chain legitimacy.
What are the consequences of relying on illegitimate certificates?
Understanding the risks helps justify the effort required for proper verification. The consequences extend far beyond simple compliance failures.
Illegitimate certificates create vulnerabilities that can devastate businesses and reputations.

What legal and financial risks do illegitimate certificates create?
Fines, shipment rejections, lost contracts, and legal liability for false claims represent significant financial exposures. A German brand faced €280,000 in retailer penalties when their supplier's certificate proved illegitimate. These risks highlight why certificate legitimacy verification is essential risk management.
How do illegitimate certificates damage brand reputation?
Consumer trust erosion, media exposure, and retailer relationship damage can have longer-term impacts than immediate financial losses. A sustainable brand lost 40% of their stock value after media exposure of certificate issues with their primary supplier. This impact demonstrates the reputational importance of certificate legitimacy.
Conclusion
A garment factory's GOTS Scope Certificate legitimacy depends on the intersection of proper issuance by authorized bodies, precise scope definition, current validity status, and multi-channel verification. True legitimacy represents not just a valid document but a verified system of compliance that withstands scrutiny from every angle. While sophisticated forgeries can replicate the appearance of legitimacy, they cannot replicate the operational reality and independent verification that genuine certification represents.
At Fumao Textiles, our GOTS Scope Certificate's legitimacy is proven through transparent verification processes, comprehensive documentation, and open facility access that demonstrates our compliance is operational rather than just paperwork. If you're ready to partner with a manufacturer whose certification legitimacy is verified rather than assumed, contact our Business Director Elaine at elaine@fumaoclothing.com. Let's build your sustainable collection on the foundation of certification you can trust completely.










