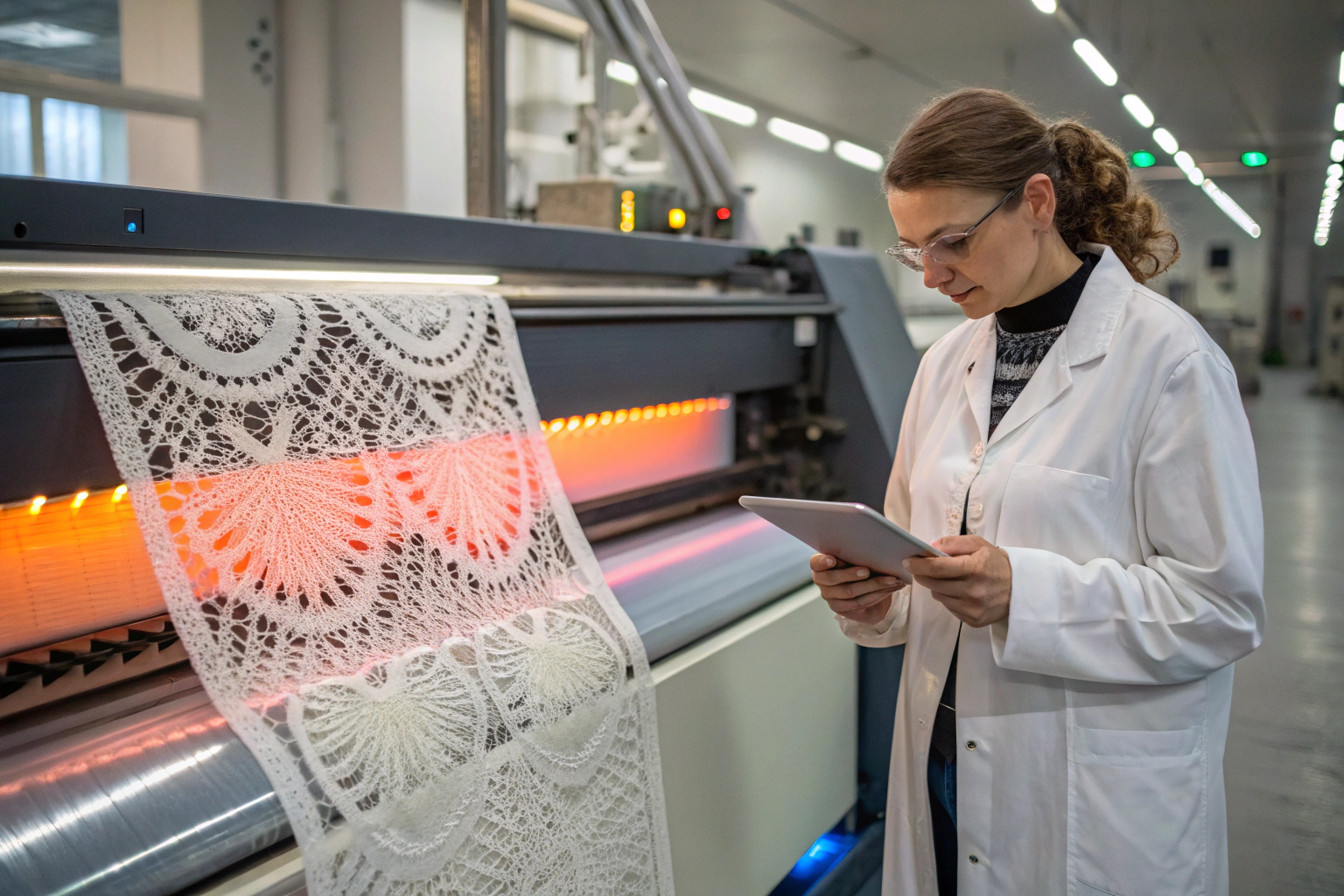
Lace. For centuries, it's been the pinnacle of luxury, painstakingly crafted by hand. But today, buyers like you are asking: in a world of automation and smart fabrics, what's next for lace? Is it destined to remain a delicate, traditional craft, or is it on the brink of a high-tech revolution that could redefine its applications and value? This question isn't just academic—it directly impacts your sourcing decisions, cost planning, and product innovation pipeline.
The future of lace is a dynamic fusion of heritage and cutting-edge technology. It's moving beyond just aesthetics into the realms of performance, personalization, and functionality. This evolution is being driven by two powerful forces: 3D printing/additive manufacturing, which allows for unprecedented structural complexity and on-demand production, and smart textile integrations, which embed interactive capabilities directly into the lace matrix. For sourcing professionals, this means lace is transitioning from a purely decorative trim to a potential centerpiece of tech-driven apparel, medical devices, and luxury wearables.
Understanding this shift is crucial. It's no longer just about comparing thread counts or floral patterns from different suppliers. The real competitive edge now lies in identifying partners who can bridge the gap between traditional craftsmanship and advanced manufacturing capabilities. Let's dive into the technologies reshaping this timeless fabric and what they mean for your next collection.
Will 3D Printing Make Traditional Lace Manufacturing Obsolete?
This is a common fear, but the reality is more about collaboration than replacement. In our 20+ years at the heart of Keqiao, we've seen numerous "disruptive" technologies come and go. 3D printing for lace isn't about making our centuries-old embroidery machines obsolete; it's about opening doors to applications that were previously impossible with thread alone. The question isn't about obsolescence, but about strategic integration.
From a sourcing perspective, 3D printing introduces radical benefits in prototyping speed and design freedom. A complex lace pattern that would take weeks to program on a traditional embroidery or Leavers machine can be 3D printed as a sample in days or even hours. This allows for rapid iteration and client approval. However, for large-scale commercial production of traditional apparel lace, the cost and speed of 3D printing are still not competitive with advanced shuttle embroidery or warp knitting. The sweet spot currently lies in high-value niches, custom details, and composite materials.
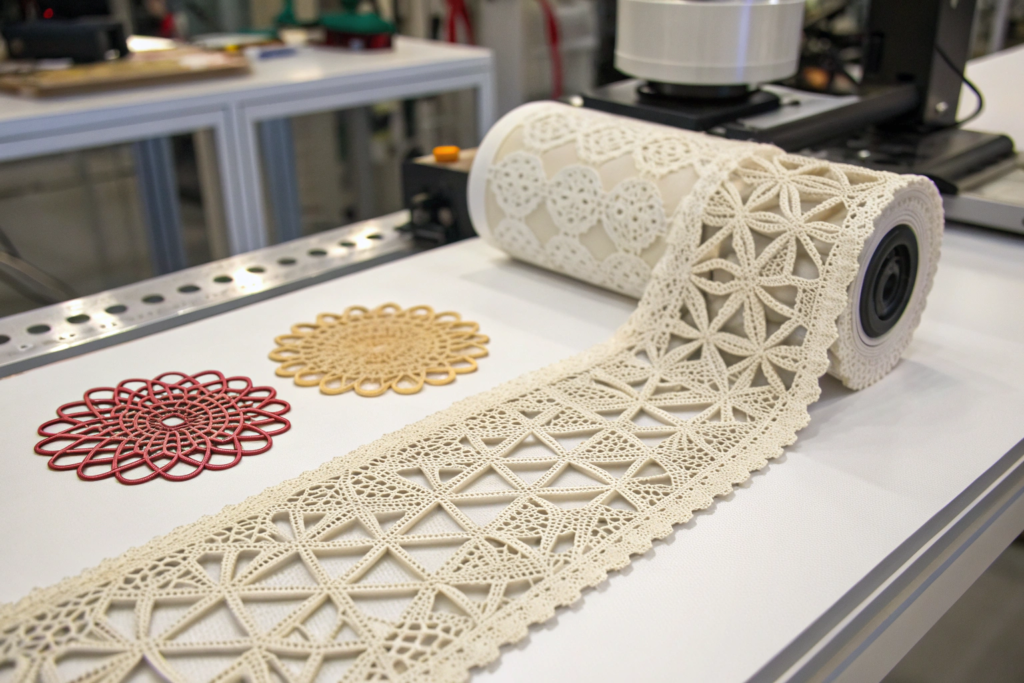
Where Does 3D Printed Lace Excel Today?
The current advantages of 3D printed lace are highly specific. It shines where traditional methods hit their limits. Architectural and structural applications are primary examples. We worked with a European haute couture house in early 2023 to create a standalone lace bodice that needed to hold its shape without an undergarment. Traditional lace would have required a complex internal corset. Instead, we used a flexible, sintered nylon powder in a collaborative 3D printing process to create a single, lightweight piece with varying densities—rigid where support was needed, and fluidly open where aesthetics demanded. The client reduced their assembly time by an estimated 60%. This kind of integrative 3D garment construction is a growing trend.
Another key area is in personalized and bespoke details. The marginal cost of altering a 3D print file is near zero, making it ideal for limited editions or incorporating unique monograms and motifs into lace designs. For brands looking into how to incorporate 3D printed textiles into luxury fashion, this is the low-risk entry point. It bypasses the massive minimum order quantities (MOQs) of traditional lace production. A useful resource for exploring these design principles is the community-driven forum Wevolver, which often features case studies on material innovations.
What Are the Limitations of 3D Printed Lace for Bulk Orders?
For the bulk orders that drive our business and yours, traditional methods still reign supreme. Let's break down the core limitations:
- Cost per Unit: The material and machine time cost for 3D printing a square meter of lace is orders of magnitude higher than producing the same area via multi-head embroidery or raschel knitting.
- Production Speed: A single 3D printer might take hours to produce a motif, while an industrial embroidery machine can produce thousands of identical motifs in the same time.
- Material Handfeel: Achieving the softness, drape, and texture of fine cotton, silk, or polyester lace threads with 3D-printed polymers remains a significant challenge. The "hand" of the fabric is often criticized as being too plastic-like for direct skin contact in garments.
Here’s a quick comparison based on our internal sampling for a mid-weight floral lace:
| Feature | Traditional (Schiffli Embroidery) | 3D Printing (Polyamide) | Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed for 10,000 motifs | ~24-48 hours | ~500+ hours | Traditional |
| Cost per motif (approx.) | $0.15 - $0.30 | $2.50 - $5.00 | Traditional |
| Design Change Flexibility | Low (new drum/patterning needed) | Very High (digital file edit) | 3D Printing |
| Material Handfeel/Drape | Excellent (soft, flexible) | Moderate (can be stiff) | Traditional |
| Structural Complexity | Limited to 2.5D embroidery | Extreme (full 3D structures) | 3D Printing |
For brands that need reliable, cost-effective, and high-quality lace sourcing, the path isn't an either-or choice. At Shanghai Fumao, our strategy is hybrid. We use 3D printing for ultra-fast prototyping and complex appliqués, then leverage our deep network of embroidery factories for bulk production. This ensures you get the design innovation without sacrificing commercial viability. A great resource to understand the scale of traditional production is exploring the capabilities of industrial embroidery machine manufacturers like Barudan or Tajima, whose technology still forms the backbone of global lace output.
How Are Smart Textiles Being Integrated into Modern Lace?
This is where the future gets truly exciting. Smart textile integration transforms lace from a passive material into an interactive interface. Imagine lace that monitors vital signs, changes color with body temperature, or incorporates subtle, glowing elements for evening wear. This isn't science fiction; it's the next frontier of functional fashion, and it requires a completely new supply chain for smart textile components.
The integration happens at multiple levels. The most common method is post-production attachment, where conductive threads, micro-LEDs, or thin sensors are carefully embroidered or adhered onto a finished lace substrate. A more advanced, and durable, method involves in-weave integration, where conductive yarns (like silver-coated polyamide) become part of the lace structure itself during knitting or embroidery. This requires close collaboration between the lace manufacturer and electronics specialists for wearable technology. The biggest challenge we face is ensuring these integrations survive washing, wear, and, crucially, the finishing processes like dyeing and steaming.
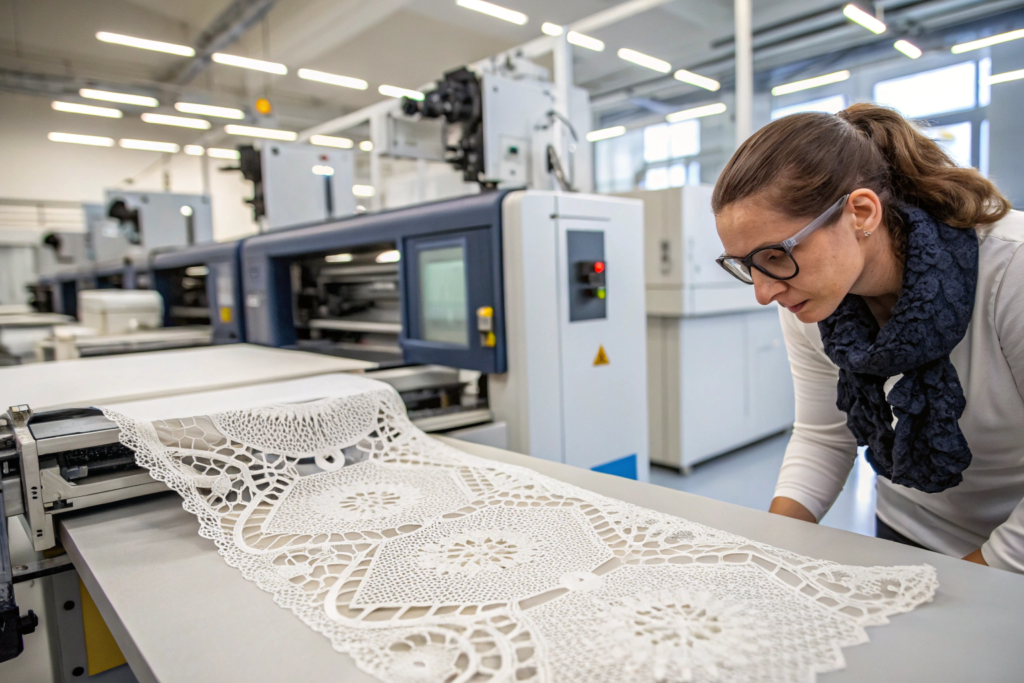

What Are the Real-World Applications of Smart Lace?
The applications move far beyond runway gimmicks. We're seeing serious interest from three key sectors:
- Medical and Wellness Wearables: This is a huge growth area. In late 2023, we developed a prototype for a US-based startup creating a comfortable, discreet labor monitoring system for expectant mothers. The challenge was creating a stretch lace belt that felt like luxury lingerie but housed embedded, flexible sensors to detect uterine activity. We sourced ultra-soft, moisture-wicking nylon lace and worked with their engineers to design a channel within the raschel knit pattern to secure the silicone-encased sensor ribbon without compromising comfort. The key was our CNAS-certified lab's ability to test the lace's durability and skin-sensitivity after the integration, ensuring safety and reliability.
- Interactive Performance and Dancewear: Here, aesthetics and function merge. Dancers and athletes need unrestricted movement, but their costumes can be central to the performance. Integrating ultra-thin, programmable LED strands into lace overlays allows for stunning visual effects. The technical hurdle is power and control. We often recommend a modular approach, where the smart lace panel connects to a small, removable power pack hidden in a seam—this makes garment care much simpler.
- High-Fashion with Function: Think of a lace gown where the pattern subtly illuminates in response to sound or touch. This requires a deep understanding of both couture construction techniques and soft circuit engineering. For brands venturing here, finding a supplier with cross-disciplinary project management is essential. The Fashion Institute of Technology's (FIT) blog on smart textiles often publishes insightful interviews with designers pushing these boundaries, which is a fantastic source of inspiration.
What Are the Key Challenges in Sourcing Smart Lace?
Sourcing smart lace isn't like ordering a standard stock item. You must be prepared for a co-development journey. The main challenges include:
- Washability and Durability: This is the number one concern. Any electronic component must be insulated and the connections must be robust. Standard industry tests like AATCC 135 for dimensional stability and AATCC 8 for colorfastness are just the starting point; you need specialized testing for electrical continuity after abrasion and washing.
- Power Supply Integration: The "how to power wearable tech discreetly" question is critical. We work with partners who specialize in miniaturized, flexible batteries and efficient, low-heat micro-LEDs to ensure the solution is practical and safe.
- Cost and MOQs: The specialized materials and labor-intensive assembly drive costs up. MOQs for truly integrated smart lace are often in the hundreds, not thousands, of meters initially. It's a premium product.
For a company like Shanghai Fumao, our role is to be the integrator and quality guarantor. We don't just supply lace; we manage the entire process: sourcing the base lace with the right mechanical properties, coordinating with our approved smart component partners, overseeing the integration in a controlled environment, and conducting the rigorous pre-shipment testing that gives you confidence. This end-to-end control is what prevents smart textile projects from becoming logistical nightmares.
Can Sustainable and High-Tech Lace Truly Coexist?
Absolutely. In fact, the most compelling innovations are at the intersection of sustainability and technology. The old notion that "eco-friendly" means rustic or basic is dead. Today's leaders demand lace that is both kind to the planet and at the cutting edge of performance. This coexistence is achieved through innovative material science and transparent, efficient production.
The drive is market-led. Our European exports of GOTS-certified organic cotton lace and lace made from recycled polyester (rPET) have grown over 30% year-on-year. But clients now ask for more: they want these sustainable base materials to also have functional properties like inherent antibacterial finishes or enhanced biodegradability under specific conditions. This is where technology serves sustainability. For example, we've developed a lace for children's wear using Tencel™ Lyocell blended with SeaCell® (which contains seaweed). The fiber is sustainably sourced, but we then apply a plant-based antimicrobial treatment in our partnered dyeing factory, reducing the need for harsh chemical washes. It's a double win.
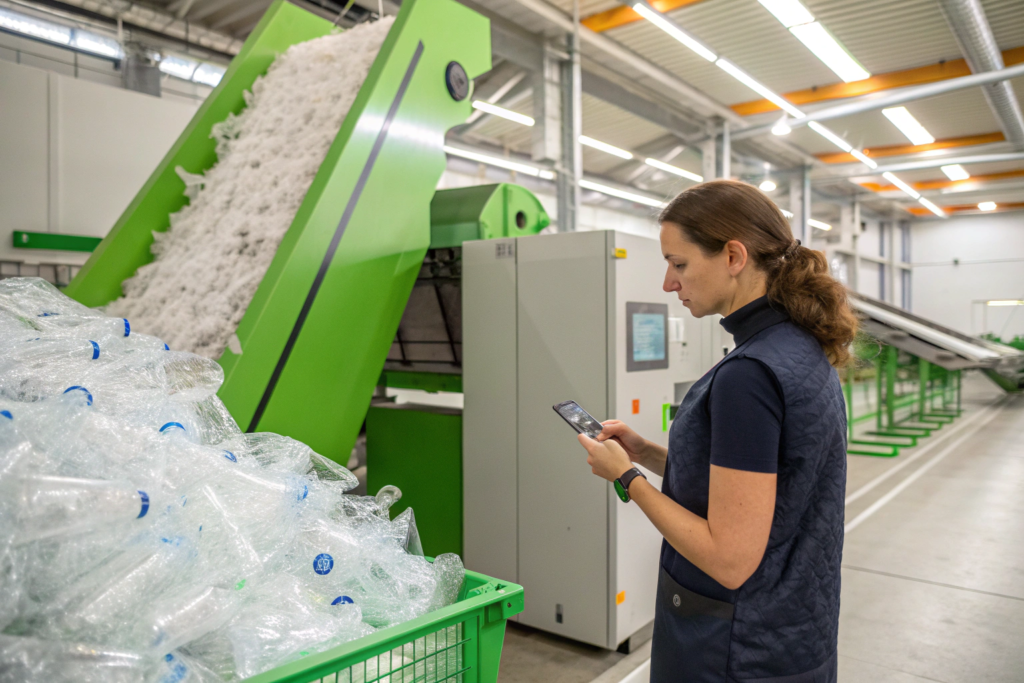

What Are the Leading Sustainable Materials for Modern Lace?
The palette of sustainable materials is expanding rapidly beyond organic cotton. Here are the front-runners we work with daily:
- Recycled Polyester (rPET): This is a powerhouse. It allows us to create durable, fine lace from post-consumer plastic bottles. The key is the quality of the recycled filament—it must be consistent enough to run on high-speed embroidery machines without breaking. We've invested heavily in sourcing top-tier rPET yarns with full traceability.
- Regenerated Celluloses (Tencel™, Modal, Cupro): These fibers, derived from sustainably harvested wood pulp, offer a gorgeous drape and silky sheen ideal for luxury lace. Their closed-loop production processes have a lower environmental impact. They also take dye beautifully, allowing for rich, vibrant colors with less chemical input.
- Biodegradable Innovations: This is the next wave. We are sampling with PLA (Polylactic Acid) lace derived from corn starch. While its heat sensitivity requires careful finishing, it offers a compelling end-of-life story for single-use applications (e.g., event décor). For brands looking into sourcing biodegradable fabrics for fashion, it's an area full of potential but requiring close supplier collaboration to manage technical constraints.
A fantastic resource for staying updated on these material innovations is the non-commercial platform Textile Exchange's Materials Hub, which provides detailed insights into the environmental profiles of different fibers.
How Does Technology Enable Transparency in Sustainable Lace?
This is a critical point. "Sustainable" claims are worthless without proof. Technology provides the verification. At Shanghai Fumao, our QR code tracking system is a game-changer. Every roll of lace we ship, especially our eco-friendly lines, comes with a unique code. Scanning it with a smartphone provides a digital dossier that includes:
- Material Origin: e.g., "Recycled PET from Ocean Cleanup-certified collectors."
- Certifications: Links to digital copies of GOTS, Oeko-Tex, or GRS certificates.
- Production Journey: Key stages and their locations (with energy usage data for our own facilities).
- Lab Test Results: Immediate access to physical property and safety tests from our CNAS lab.
This level of blockchain-adjacent supply chain transparency is what empowers you, the buyer, to make verified claims to your own customers. It turns a sustainability promise into a tangible, marketable asset. This system helped a UK-based eco-luxury brand we partnered with in 2022 to successfully pass a rigorous brand audit by a major department store, securing them a coveted retail listing.
How to Plan Your Sourcing Around Chinese Production Cycles for Lace?
This might seem like a logistical question, but it's fundamentally a strategic one that determines your profitability and market success. You can have the most innovative 3D-printed, smart, sustainable lace design, but if you miss the production window, it's worthless. Understanding the rhythm of China's manufacturing calendar is non-negotiable. Based on two decades of navigating these cycles in Keqiao, I can tell you that proactivity is your single greatest asset.
The Chinese production calendar has predictable peaks and valleys that directly impact lead times, costs, and quality. The peak production periods (March-May and August-October) see factories at full capacity. During this time, adding 1-2 weeks to standard timelines is prudent for complex items like intricate lace. The holiday shutdowns (Chinese New Year - 3-4 weeks, Golden Week - 1 week) require advanced planning—your order must be in the queue well before the factory closes. Conversely, the slower periods (June-July, November-December) can offer timeline advantages and sometimes more negotiating power on price, as factories seek to fill their capacity.

What Is the Critical Path for Lace Orders Before Chinese New Year?
Chinese New Year (CNY) is the most significant disruption. A European fashion brand we work with now has this down to a science: they complete all pre-production (final lab dips, approved strike-offs, and lace embellishment approvals) a full 6 weeks before the holiday. This ensures their production order is first in line when factories reopen. Here's a sample critical path for a Spring/Summer lace collection needing a CNY shipment:
- T-12 Weeks (Early Nov): Finalize all designs, tech packs, and submit for sampling. This is the time for lace pattern development and initial sampling.
- T-10 Weeks (Mid-Nov): Receive first lace samples. Conduct fit and quality reviews. (Here I have to interject, our 48-hour rapid sampling for lace edits really saves the day here).
- T-8 Weeks (Early Dec): Approve final samples and lab dips. Place firm bulk production order and make the deposit. This is the absolute latest to secure a pre-CNY slot.
- T-6 Weeks (Mid-Dec): All materials (yarns, dyes) must be confirmed at the factory. Pre-production meeting.
- CNY Closure (Late Jan): Factory shuts down.
- Factory Reopening (Mid-Late Feb): Production starts immediately on your order.
- Shipment (Late March): Goods completed and shipped.
Missing the T-8 week deadline often means your order gets pushed to after CNY, potentially delaying your shipment by 5-7 weeks. For a deeper dive into navigating these timelines, the sourcing blog ChinaImportal offers excellent, practical guides on production planning.
How Can You Leverage Slower Periods for Development and Advantage?
Smart buyers use the slower periods (June-July, Nov-Dec post-rush) strategically. This is the ideal time for:
- New Supplier Qualification: Factories have more time for tours and meetings. You can audit their lace-making equipment and quality control processes thoroughly.
- Complex Development Work: Working on that integrated smart lace or 3D printed composite? The slower pace means engineers and technicians can give your project more focused attention, leading to better outcomes.
- Negotiating for Q1 Production: Placing orders in November/December for production in January/February (pre-CNY) can sometimes secure better pricing, as factories are eager to book their Q1 capacity early.
A key lesson from a client in New York: In November 2022, during a slower period, they commissioned us to develop a new heat-transfer printed lace technique. Because our R&D team wasn't swamped, we achieved the desired opacity and handfeel in just 3 sample rounds instead of the typical 5. This gave them a unique product for their Fall collection, all because they used the "off-season" for innovation, not just passive waiting.
Conclusion
The future of lace is not a single path, but a vibrant crossroads where tradition meets technology, and sustainability meets smart functionality. For sourcing professionals, this complexity is an opportunity, not a obstacle. The brands that will lead are those that partner with suppliers who understand both the artistry of a Leavers lace machine and the programming of a 3D printer, who can source GOTS-certified organic cotton and also integrate a micro-LED circuit.
It's about moving beyond transactional purchasing to collaborative development. Whether your interest lies in the structural possibilities of 3D printing, the interactive potential of smart textiles, the verified credentials of sustainable materials, or simply the timeless need for flawless execution on a tight calendar, the principle remains the same: success depends on a deep, strategic partnership with your supplier.
At Shanghai Fumao, this is the future we are building every day from the heart of Keqiao. We weave the world's style by connecting 20 years of textile mastery with tomorrow's innovations. If you are ready to explore how these future-facing lace technologies can be applied to your next collection—from a small, groundbreaking sample to a full-scale commercial order—we have the expertise, the network, and the agility to make it happen. Let's co-create the future of your brand's textiles. To discuss your specific project needs and timelines, we recommend reaching out directly to our Business Director, Elaine. She can guide you through our capabilities and initiate the development process. You can contact her at: elaine@fumaoclothing.com.










