Flame retardancy is a top priority in many sectors of the textile industry, from children’s sleepwear to industrial uniforms and upholstery. However, traditional flame retardants often come with a toxic legacy—halogenated chemicals and heavy metals that pose serious health and environmental risks. The global industry is now pivoting to safer, sustainable alternatives.
Among these innovations, plant-based flame retardants are gaining traction as eco-conscious, biodegradable solutions that align with strict global standards. For fabric buyers and apparel brands committed to sustainability, understanding this evolving market is key.
In this article, we explore where plant-based flame retardants are headed, how they compare to chemical solutions, which bio-sources are being used, and how manufacturers like Fumao Fabric integrate them into scalable textile production.
Which Plants Are Used to Create Flame Retardant Agents?
Plant-based retardants don’t come from a single extract—they are derived from an expanding range of agricultural waste and bio-compounds. These include banana peels, phytic acid (from cereals), lignin (from wood), and even pomegranate peel.
These sources provide phosphorus, nitrogen, and tannins—all key elements in creating a fire barrier on natural or synthetic textiles.
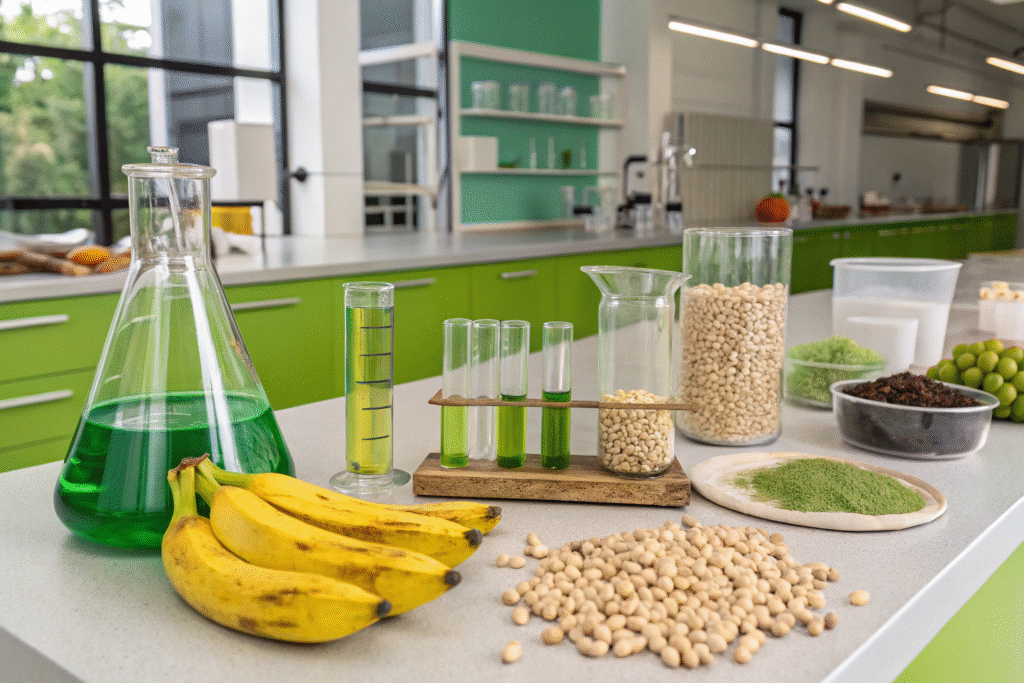

Why Is Phytic Acid a Promising Bio-Retardant?
Phytic acid, found in grains and legumes, is rich in phosphorus, which helps form a protective char layer when exposed to heat. Researchers have found that coating cotton with phytic acid-based compounds can drastically reduce flammability without affecting softness or breathability.
Explore this scientific study on phytic acid flame retardants or view material safety profiles here.
How Effective Are Lignin and Tannin-Based Retardants?
Lignin, a byproduct of the paper industry, is a natural flame suppressant. It works by increasing char formation and reducing volatile gas release. Tannins, abundant in bark and fruit skins, can enhance lignin's action when used in hybrid coatings.
Read about lignin’s flame retardant properties or discover tannin-based textile applications.
How Do Bio-Based Flame Retardants Perform vs Chemical Ones?
One of the most common concerns from industrial buyers is whether bio-based solutions are as effective as their synthetic counterparts. The answer is—it depends on the application.
For cotton, rayon, and modal, plant-based retardants like phytic acid and bio-phosphates offer flame spread reductions similar to ammonium phosphate-based treatments. For synthetics like polyester, hybrid solutions or multi-step treatments may be necessary.
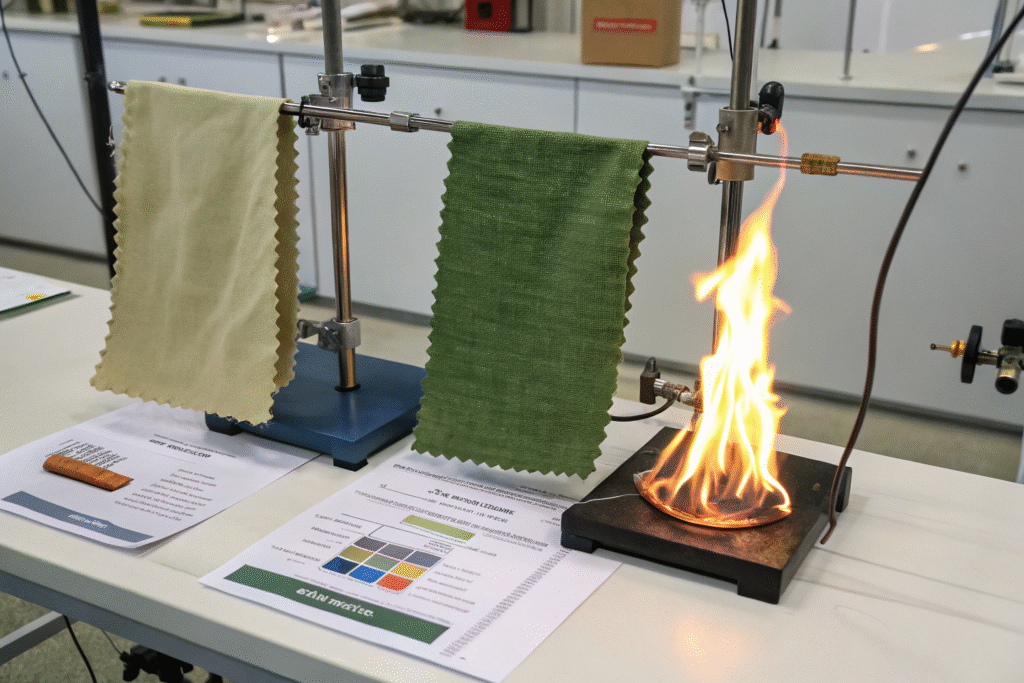
What Are the Key Metrics of Comparison?
| Property | Plant-Based Retardants | Synthetic Retardants |
|---|---|---|
| Eco-Toxicity | Low | High (some are banned) |
| Biodegradability | High | Low |
| Flame Spread Control | Moderate–High (on cotton) | Very High |
| Durability (wash cycles) | Moderate (10–15 washes) | High (20–50 washes) |
| Cost (per kg) | Slightly Higher | Lower |
Compare bio vs chemical solutions in this textile sustainability guide or read global market reports.
Can Plant-Based Retardants Be Used Commercially?
Yes. With modern binders and coating technologies, bio-retardants have moved beyond lab prototypes. For example, our team at Fumao Fabric has already implemented lignin-phytic acid dual coatings for children’s wear exports that pass BS EN 14878 and CFR 1615/1616 standards.
View examples of commercial bio-retardant textile products or certification protocols.
What Are the Safety & Certification Requirements?
Even natural flame retardants need validation. Regulatory bodies still require performance testing, toxicology data, and chemical disclosure before market entry. In the EU, REACH and GOTS guidelines apply. In the U.S., buyers reference NFPA 701, CFR 1610, and California Technical Bulletin 117-2013.
We at Fumao support buyers with ready-to-submit documentation packs for each treated fabric.

What Tests Are Required for Flame Retardant Approval?
Here are typical tests used in approval pipelines:
| Standard/Test Code | Region | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| NFPA 701 | USA | Flame propagation |
| BS EN 14878 | EU | Children’s nightwear flammability |
| ISO 15025 | International | Protective clothing |
| OEKO-TEX 100 | Global | Toxicological compliance |
| California TB 117 | USA | Upholstery textile testing |
Check specific NFPA textile codes or OEKO-TEX certification tools.
How Does Fumao Fabric Ensure Certification Integrity?
We operate a CNAS-certified internal lab and partner with ITS and SGS to validate all flame retardant treatments. Our QR traceability system links each batch to its test results, formulation sheet, and shipping documents—easing import and customs clearance.
Learn how CNAS labs work or browse SGS textile services.
Where Can You Source Bio Flame-Retardant Fabrics?
There are still few suppliers in the world who can offer bio flame-retardant fabrics at commercial scale. Most R&D is done in university labs or niche startups. But at Fumao Fabric, we’ve already deployed pilot-to-bulk workflows for buyers in Europe and the USA.
We use vertical integration: fabric weaving, bio-coating, testing, and export under one umbrella—with MOQ starting from just 500 meters.
Why Is Keqiao Leading in This Innovation?
Keqiao is the global hub for textile development, home to 80,000+ companies, including ours. We’ve built partnerships with local biotech labs and coating factories to scale up eco-retardants safely. The “Silk Road Keqiao” initiative also allows for smoother customs clearance and warehouse delivery in the EU.
Learn more about Keqiao’s textile strength or our vertical production workflow.
What Should You Ask When Contacting a Supplier?
When contacting suppliers, ask:
- What is the flame retardant ingredient?
- Is it GOTS/REACH/NFPA compliant?
- What test results can you provide?
- How many wash cycles does it last?
- Can you customize the fabric weight/feel?
At Fumao, we answer all of the above and support your project from concept to shipment, including sample cutting, third-party testing, and private labeling.
Check our live fabric collection at Fumao Fabric Website or connect on Alibaba Trade Show.
Conclusion
As the textile industry shifts toward sustainable performance materials, plant-based flame retardants offer a green path forward without sacrificing safety. With raw materials sourced from banana skins, grains, and lignin—and performance standards already matching traditional chemicals—this innovation is now ready for global production.
Whether you’re developing certified school uniforms, eco-friendly upholstery, or fire-rated fashion, Fumao Fabric provides a complete, transparent solution for your sourcing needs. Our vertically integrated system ensures that your fabrics are not only safe and stylish—but also compliant and scalable.
Interested in using bio flame retardants in your next production run? Contact our Business Director Elaine at elaine@fumaoclothing.com. Let's bring the future of safe, sustainable textiles to your customers together.










