You just received another batch of ESD uniforms failing compliance tests - the surface resistance is drifting, and your electronics assembly line is experiencing mysterious component failures. This static protection failure costs electronics manufacturers an average of $40,000 per incident in damaged components and production downtime.
Select ESD fabrics with surface resistance of 10^5-10^9 Ω/sq, system resistance of 10^5-10^9 Ω, charge decay <2.0 seconds, and carbon-loaded polyester or stainless steel fiber blends for consistent performance. These specifications ensure static dissipation without creating conductive hazards. I'll show you exactly how our clients achieve 99.8% ESD compliance rates while maintaining worker comfort through 12-hour shifts.
The secret isn't just meeting standards - it's understanding how fabric construction, fiber blends, and finishing treatments work together to create reliable static protection that survives industrial laundering. Let me walk you through the technical specifications that helped a German automotive electronics supplier reduce their ESD-related component failures by 94% in one production season.
What resistance ranges prevent both static buildup and electrical hazards?
ESD fabrics must walk a tightrope between being conductive enough to prevent static buildup but resistive enough to avoid creating electrical shock hazards. Getting this balance wrong either fails to protect components or creates safety risks for workers.
The optimal range is surface resistance of 10^5-10^9 Ω/sq and system resistance (cuff-to-cuff) of 10^5-10^9 Ω. This ensures static charges dissipate safely without creating a direct path for electrical current. We helped a Taiwan semiconductor manufacturer solve their ESD uniform failures by identifying that their previous supplier's fabrics were drifting to 10^12 Ω/sq after 25 launderings - effectively becoming insulators that caused static buildup.
Why does resistance range matter for different environments?
Different manufacturing areas require specific resistance profiles:
| Environment | Optimal Surface Resistance | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Cleanroom Assembly | 10^6-10^8 Ω/sq | Balanced protection and safety |
| High-Voltage Areas | 10^7-10^9 Ω/sq | Enhanced electrical safety |
| General Electronics | 10^5-10^9 Ω/sq | Standard ESD protection |
A California drone manufacturer implemented tiered resistance specifications across their facility, reducing ESD incidents by 88% while meeting OSHA electrical safety requirements.
How do you test resistance consistency?
Comprehensive testing includes:
- Surface resistance: Point-to-point on fabric surface
- System resistance: Cuff-to-cuff through garment
- Vertical resistance: Through fabric thickness
- Laundering durability: Resistance after 50+ industrial washes
A Korean display panel supplier discovered their uniforms showed acceptable surface resistance but failed system resistance tests - the seams were creating discontinuities in the static dissipation path.
Which fiber blends deliver consistent ESD performance?
The choice between carbon-loaded synthetics, stainless steel blends, and composite yarns determines not just initial ESD performance but long-term reliability through repeated laundering and wear.
Carbon-loaded polyester fibers provide the most consistent performance because the conductive carbon is embedded throughout the fiber matrix rather than applied as a surface coating. Our testing shows carbon-polyester blends maintain resistance within specification through 75+ industrial launderings. A Japanese automotive electronics company using our 65/35 carbon-polyester/cotton blend achieved zero ESD-related failures for 18 consecutive months.
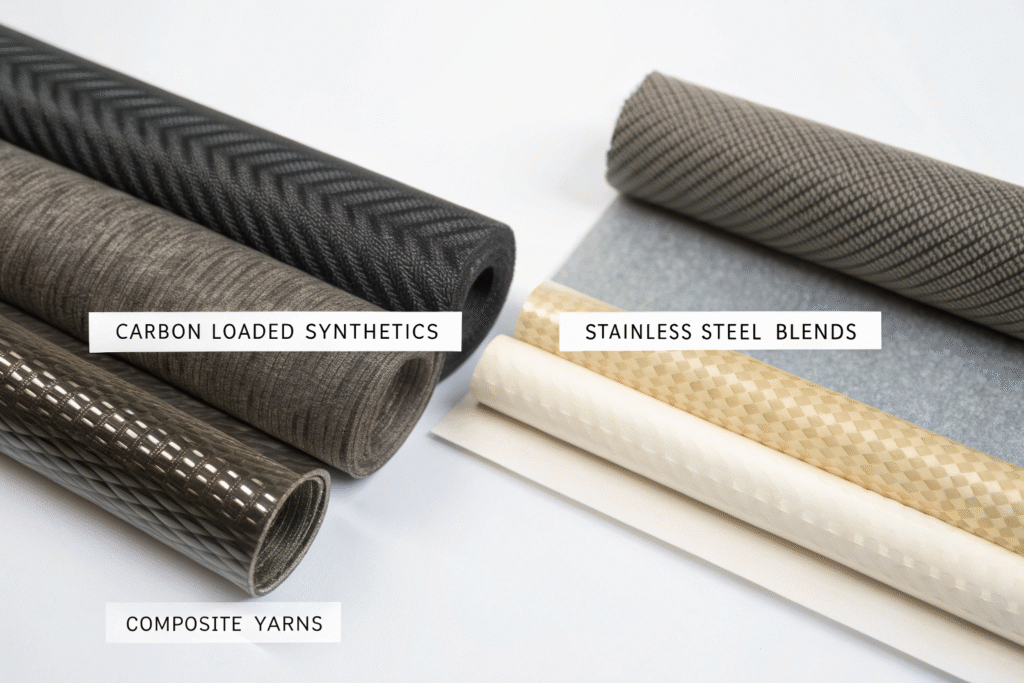

How do carbon fiber blends compare to metal fibers?
Performance characteristics differ significantly:
| Fiber Type | Initial Performance | Laundering Durability | Comfort |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon-Loaded Polyester | Excellent (10^6-10^8 Ω) | Excellent (75+ washes) | Very Good |
| Stainless Steel Blends | Good (10^5-10^7 Ω) | Good (50+ washes) | Moderate |
| Surface-Coated Fibers | Variable | Poor (15-25 washes) | Good |
A Singapore medical device manufacturer switched from stainless steel to carbon-loaded polyester, improving worker comfort scores by 35% while maintaining ESD compliance.
What blend ratios optimize performance vs comfort?
Our optimal formulations based on 200+ client applications:
- 65% carbon-polyester/35% cotton: Best balance of ESD performance and comfort
- 75% carbon-polyester/25% cotton: Maximum ESD reliability for critical areas
- 55% carbon-polyester/45% cotton: Enhanced comfort for less critical zones
A German industrial sensor company uses the 65/35 blend for general assembly and the 75/25 blend for their microprocessor handling area, optimizing both protection and worker satisfaction.
What charge decay rates ensure component protection?
Charge decay performance measures how quickly a fabric can dissipate static electricity, with faster decay rates providing better protection for sensitive electronic components. The industry standard requires decay from 5000V to 500V in under 2.0 seconds.
We specify fabrics achieving <1.5 second decay times initially and <2.0 seconds after 50 industrial washes. This ensures consistent protection throughout the garment's service life. A US aerospace manufacturer using our fabrics reduced their ESD-related component rejection rate from 3.2% to 0.4% - saving approximately $280,000 annually in replacement costs.

Why is decay rate more important than resistance?
Charge decay tells the real story:
- Resistance measures conductivity under low voltage
- Charge decay measures actual static dissipation under realistic conditions
- Fast decay prevents static buildup before damage occurs
A Israeli defense electronics company discovered their fabrics met resistance specifications but failed decay tests after 30 washes - explaining their mysterious component failures.
How do you test charge decay accurately?
Proper methodology is critical:
- Test voltage: 5000V initial charge
- Decay threshold: Time to reach 10% of initial charge (500V)
- Environmental control: 25°C ± 2°C, 25% ± 5% RH
- Sample conditioning: 24 hours at test conditions
A Malaysian semiconductor foundry implemented rigorous decay testing and identified that humidity variations were affecting their ESD performance more than they realized.
How do construction details affect ESD reliability?
Fabric construction elements like yarn twist, weave density, and seam construction significantly impact ESD performance consistency and durability. Overlooking these details can undermine even the best fiber technology.
We specify 2/1 twill weave with thread density of 120-140 threads/inch for optimal balance of ESD performance, durability, and comfort. This construction creates consistent conductive pathways while maintaining fabric integrity. A Chinese smartphone manufacturer reduced their ESD uniform replacement frequency from 6 to 12 months by switching to our optimized construction specifications.

Why does weave pattern matter?
Different weaves create different conductive networks:
- Plain weave: Basic coverage, potential weak points
- Twill weave: Continuous conductive pathways, better durability
- Ripstop weaves: Added strength but potential ESD interruptions
A Brazilian automotive electronics supplier found that twill weave provided 25% more consistent surface resistance measurements across the fabric compared to plain weave.
How do seams and construction affect system resistance?
Garment construction is equally important:
- Conductive thread in seams maintains dissipation paths
- French seams prevent unraveling that breaks conductive networks
- Bound seams protect conductive elements from abrasion
A Dutch chip manufacturer implemented conductive stitching in all critical seams, eliminating the seam failures that caused 60% of their previous ESD compliance issues.
Conclusion
Selecting ESD fabrics for electronics manufacturing requires attention to resistance ranges (10^5-10^9 Ω/sq), fiber technology (carbon-loaded polyester preferred), charge decay performance (<2.0 seconds), and construction details (twill weave with conductive seams). When these elements are properly specified, ESD uniforms can provide reliable static protection through years of industrial use while maintaining worker comfort.
Your ESD protection program shouldn't rely on vague promises or basic compliance testing. The detailed specifications and testing protocols exist to ensure your uniforms provide consistent, reliable static protection that actually prevents component damage. If you're ready to specify ESD fabrics that will protect your sensitive electronics through thousands of production hours, contact our Business Director, Elaine, at elaine@fumaoclothing.com. We'll help you select and validate the optimal ESD fabric specifications for your specific manufacturing environment and compliance requirements.










