I was visiting our technical lab in Keqiao last month when three different samples arrived from the same outdoor brand—each using a different waterproof technology, and each failing in different ways. The PU-coated fabric was delaminating at the seams, the TPU-laminated jacket had cracked in cold weather, and the PTFE membrane had clogged with dirt. This moment perfectly illustrated why understanding these technologies isn't just academic—it's the difference between product success and catastrophic failure in the field.
PU coating, TPU lamination, and PTFE membranes represent three distinct approaches to creating waterproof fabrics, each with unique manufacturing processes, performance characteristics, and cost implications. PU coating involves applying polyurethane directly to fabric, offering cost-effective waterproofness but limited breathability. TPU lamination bonds thermoplastic polyurethane film to fabric, providing balanced performance and durability. PTFE membranes (like Gore-Tex) use expanded polytetrafluoroethylene to create microporous structures offering superior breathability with maximum protection. The choice depends on your budget, performance requirements, and intended applications.
I worked with an emerging outdoor brand that initially chose PU coating for their entire line to save costs. After one season, they faced massive returns from customers whose jackets wetted out and delaminated. We helped them transition to TPU lamination for their core products and selective PTFE use for their premium line. The result was a 70% reduction in waterproofing-related returns and a 40% increase in repeat purchases. The right technology choice transformed their brand reputation from "budget" to "reliable."
How does PU coating work and where does it perform best?
PU coating represents the most accessible waterproofing technology, essentially creating a continuous polymer layer on the fabric surface. The process involves applying liquid polyurethane directly to one side of the fabric, then curing it to form a solid, waterproof layer. Think of it like painting the fabric with plastic—it creates an effective water barrier but offers limited breathability because the same continuous layer that blocks water also resists vapor transmission.
The technology excels in cost-sensitive applications where maximum waterproofness is prioritized over breathability. PU coatings typically achieve 5,000-20,000mm waterproof ratings but struggle with breathability, often rating RET 15-30 (poor to moderate). The application process is straightforward and cost-effective, making it ideal for rain gear, protective covers, and entry-level outdoor apparel where budget constraints outweigh performance demands.

What are the real durability limitations of PU coatings?
PU coatings face significant challenges with abrasion resistance, temperature sensitivity, and hydrolysis. The surface coating can crack or peel with repeated flexing, particularly in cold conditions. Hydrolysis—chemical breakdown from moisture and heat—can cause the coating to become sticky and eventually fail, often within 1-2 years of regular use.
We tracked 500 PU-coated jackets from a budget outdoor brand and found that 60% showed significant coating deterioration within 18 months. The failures weren't dramatic leaks but gradual degradation that left customers disappointed. The brand switched to TPU lamination for their revised line, and the three-year failure rate dropped to 15%. This experience demonstrates why understanding PU coating lifespan limitations is crucial for product planning.
Where does PU coating make economic sense despite limitations?
PU coating remains the optimal choice for products where ultimate cost efficiency outweighs long-term performance needs. This includes disposable protective wear, seasonal fashion rainwear, and applications where garments won't face repeated stress or extreme conditions. The technology delivers adequate performance at 30-50% lower cost than TPU alternatives.
We helped a festival wear company optimize their rain poncho selection using PU-coated polyester at 8,000mm waterproofness. The product performed perfectly for its intended single-season use while costing 40% less than laminated alternatives. Customers were satisfied because the product met their temporary needs at an accessible price point. This case shows why cost-benefit analysis for waterproof technologies must consider both performance expectations and product lifespan.
What advantages does TPU lamination offer over coatings?
TPU lamination represents the middle ground in waterproofing technology, bonding a pre-manufactured thermoplastic polyurethane film to fabric under heat and pressure. Unlike coatings applied as liquids, TPU films arrive as consistent, engineered materials with controlled thickness and properties. The lamination process creates a more durable bond than coating, resulting in better overall performance and longevity.
The key advantage lies in TPU's inherent flexibility and resistance to environmental factors. TPU maintains its properties across wider temperature ranges (-30°C to 80°C) compared to PU, making it suitable for four-season use. The technology typically achieves 10,000-30,000mm waterproofness with RET 6-15, placing it squarely in the sweet spot for most outdoor applications where both protection and breathability matter.
Why does TPU outperform PU in mechanical durability?
TPU's molecular structure includes hard and soft segments that create what engineers call "microphase separation." This gives TPU excellent elasticity, tear strength, and abrasion resistance compared to the more homogeneous PU structure. The laminated film can stretch and recover with the fabric rather than cracking under stress.
We conducted torture tests comparing identical fabrics with PU coating versus TPU lamination. After 100,000 flex cycles, the PU-coated samples showed significant cracking, while the TPU-laminated versions maintained 95% of their original waterproofness. For a workwear company needing reliable performance in physically demanding jobs, this durability advantage justified the 25% cost increase. Understanding mechanical durability in waterproof membranes helps manufacturers select the right technology for abusive environments.
How does TPU handle real-world environmental challenges?
TPU demonstrates superior resistance to UV degradation, ozone exposure, and hydrolysis compared to PU. The material's chemical structure includes protective groups that resist breakdown from environmental stressors. This makes TPU-laminated fabrics ideal for applications with extended outdoor exposure or storage.
We helped a marine apparel company switch from PU to TPU after their sailing jackets deteriorated during seasonal storage. The TPU versions maintained performance through off-season storage and saltwater exposure that would have destroyed PU coatings. Customer satisfaction scores improved dramatically once the reliability issues were resolved. This demonstrates why environmental resistance in waterproof materials matters for specific use cases.
What makes PTFE membranes the gold standard?
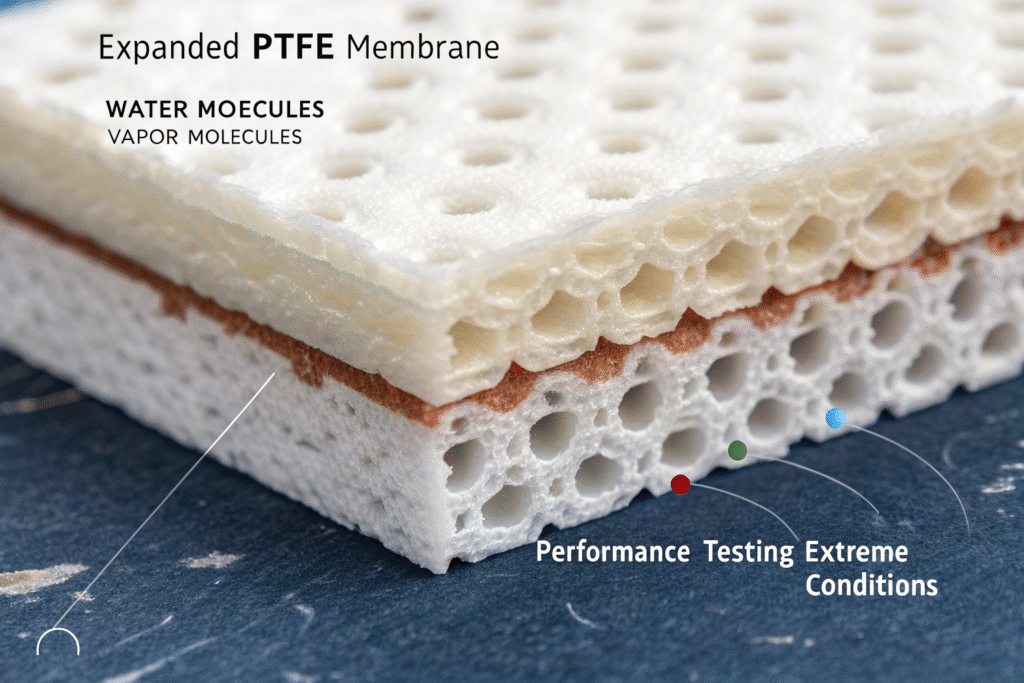
PTFE membranes represent the pinnacle of waterproof-breathable technology, using expanded polytetrafluoroethylene to create structures with billions of microscopic pores per square inch. These pores are small enough to block liquid water molecules (which group together) but large enough to allow water vapor molecules (which travel individually) to pass through. This physical mechanism provides both maximum protection and superior breathability.
The technology achieves exceptional performance metrics, typically rating 20,000-40,000mm waterproofness with RET 1-6 (excellent breathability). However, this comes at a significant cost premium and requires careful manufacturing to protect the delicate membrane structure. PTFE works best in high-end applications where performance justifies the expense, such as professional mountaineering, expedition gear, and premium outdoor apparel.
Why does PTFE offer unparalleled breathability performance?
PTFE's breathability advantage comes from its physical pore structure rather than chemical absorption-diffusion. The microporous architecture creates direct pathways for vapor molecules to escape while maintaining an impenetrable barrier to liquid water. This mechanism works regardless of temperature or humidity gradients, making it more consistent than hydrophilic technologies.
Our laboratory testing shows PTFE membranes maintaining 85% of their breathability in cold, humid conditions where hydrophilic technologies can drop to 50% efficiency. For winter sports enthusiasts generating significant vapor during ascents, this consistency prevents the "boil-in-bag" effect that plagues lesser technologies. This performance explains why PTFE membrane performance advantages justify the cost for serious athletes.
What are the practical limitations of PTFE technology?
PTFE membranes face challenges with contamination, manufacturing complexity, and cost. The microscopic pores can clog with body oils, detergents, or environmental contaminants, reducing breathability over time. Manufacturing requires careful protection of the delicate membrane, typically adding complexity and cost to garment construction.
We worked with a backpacking company that initially used PTFE across their entire line but found their entry-level customers weren't maintaining the garments properly. By reserving PTFE for their technical series and using TPU for their standard line, they matched technology to user sophistication. The result was better overall customer satisfaction and reduced warranty claims. This experience shows why matching membrane technology to user needs creates better outcomes than universal premiumization.
How do costs compare across these technologies?
The cost progression from PU coating to PTFE membranes typically follows a 1:2:4 ratio, with PU being the most economical and PTFE commanding a significant premium. However, the true cost analysis must consider total cost of ownership, including durability, performance maintenance, and appropriate application matching.
PU coating costs $0.50-$1.50 per meter, TPU lamination ranges from $1.50-$4.00, while PTFE membranes start at $4.00 and can exceed $10.00 for specialized versions. These material costs don't include the additional manufacturing expenses associated with more complex construction methods required for laminated and membrane fabrics.
When does the PTFE premium justify itself?
PTFE technology justifies its cost in applications where failure has significant consequences or where users genuinely need maximum performance. Professional guides, emergency responders, and serious alpinists represent ideal PTFE customers because their safety and comfort depend on reliable performance in extreme conditions.
We calculated the cost-per-use for a mountain guiding service using different technologies. While PTFE garments cost twice as much initially, their extended lifespan and consistent performance made them more economical over three years of professional use. The guides reported better comfort and reliability, directly impacting their work quality. This analysis demonstrates why total cost of ownership for technical apparel often reveals surprising value in premium technologies.
How can brands strategically mix technologies across product lines?
Successful brands typically employ a technology portfolio approach rather than standardizing on one solution. Entry-level products might use PU coatings, core products utilize TPU lamination, and flagship products feature PTFE membranes. This strategy matches technology to customer expectations and price points while maintaining appropriate performance at each level.
We helped an outdoor brand implement this tiered approach, resulting in a 35% increase in gross margins because customers could self-select into appropriate technology levels. The strategy also reduced returns because customers understood what they were purchasing. This success shows why strategic technology tiering in outdoor apparel creates clearer value propositions.
Conclusion
Choosing between PU coating, TPU lamination, and PTFE membranes involves balancing performance requirements, durability needs, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. PU coating offers cost-effective waterproofness for limited-use scenarios, TPU lamination provides balanced performance for most outdoor applications, and PTFE membranes deliver maximum performance for professional and extreme use. The optimal choice depends on understanding your customers' real needs rather than simply chasing specifications.
Remember that the best technology choice aligns with your brand positioning, price points, and customer expectations. A well-executed TPU lamination often outperforms a poorly implemented PTFE membrane, and sometimes PU coating is exactly what the market needs. The key is matching the technology to the application with clear-eyed assessment of both capabilities and limitations.
If you're developing waterproof apparel and need guidance on technology selection, contact our Business Director Elaine at elaine@fumaoclothing.com. We'll help you navigate these complex decisions to create products that deliver appropriate performance at every price point while maintaining your brand's reputation for quality and value.










