As a fabric supplier with over two decades in the textile industry, I've seen too many orders get rejected because of improper fabric shrinkage control. It's a common pain point for buyers like you, especially when shipping from China to the U.S. You need reliable, consistent fabric that won't surprise you after the first wash.
Fabric shrinkage measurement and washing standard setting are systematic processes that involve precise testing protocols, international standards, and practical application guidelines. By implementing a rigorous system from lab testing to production control, you can effectively minimize shrinkage-related defects and ensure your final garments meet size specifications consistently.
Understanding and controlling fabric shrinkage isn't just a technical requirement—it's crucial for maintaining your brand's reputation. Let's explore how you can implement effective shrinkage control measures that protect your investment and satisfy your customers.
What is the standard method for measuring fabric shrinkage?
The shrinkage percentage that appears on your fabric's test report doesn't come from guesswork. It's derived from a scientific process that follows international standards. At our CNAS-accredited lab, we adhere to proven methods that give you accurate, reliable data for your production planning.
The standard method for measuring fabric shrinkage involves marking a fabric sample, subjecting it to specific washing conditions, then measuring dimensional changes to calculate shrinkage percentage. This process follows international standards like ISO 5077 and AATCC 135, which specify marking precise distances on fabric (usually 50cm x 50cm), washing under controlled conditions, drying, and then re-measuring to determine how much the fabric has shrunk. The result is expressed as a percentage of dimensional change, which becomes critical data for your pattern making and grading decisions.
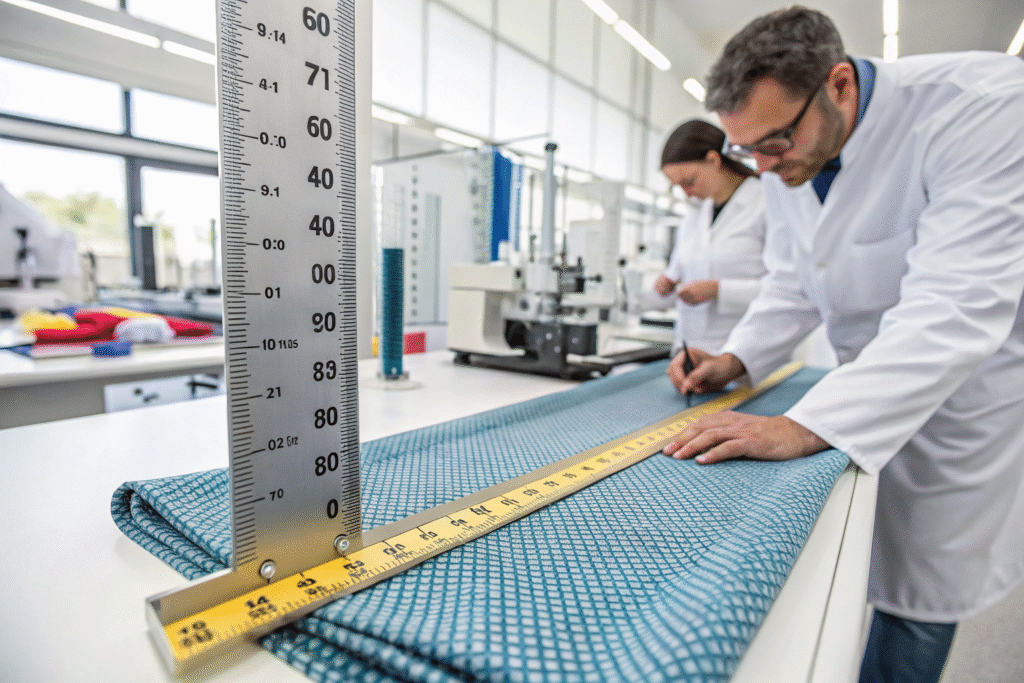

Why do different fabrics shrink differently?
The fundamental reason lies in fiber structure and fabric construction. Natural fibers like cotton and wool shrink more than synthetics because their molecular structures swell with water absorption and then contract during drying. When you understand why shrinkage occurs, you can make better fabric selection decisions for your specific applications.
- Fiber Behavior: Natural fibers have scales and twists that relax and contract when exposed to moisture and heat. Cotton can shrink up to 10% without proper pre-treatment, while wool's complex structure requires special processes like superwash treatment to minimize felting shrinkage.
- Construction Factors: Woven fabrics generally shrink less than knits due to their stable structure. However, tension during weaving and finishing can create "relaxation shrinkage" when released during washing. The fabric's thread count, yarn twist, and weave tightness all contribute to its shrinkage potential.
- Finishing Processes: Many shrinkage issues can be resolved through proper finishing. Our partnership with specialized dyeing and finishing facilities implements compressive shrinkage systems (like Sanforization for cottons) and heat-setting for synthetics to stabilize fabrics before they reach your production line.
How can you implement accurate shrinkage testing?
Establishing a reliable testing protocol requires attention to environmental conditions, equipment calibration, and consistent methodology. Even with limited resources, you can implement basic testing that protects your garments from excessive shrinkage.
| Testing Factor | Ideal Standard | Practical Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Marking Distance | 50cm x 50cm | Can use 25cm x 25cm for smaller samples |
| Washing Temperature | Varies by fabric type | Follow care instructions planned for garment |
| Drying Method | Tumble dry, line dry, or flat dry | Match your customer's expected care methods |
| Measurement Precision | To the nearest 0.1cm | Use precise rulers or digital measurement tools |
| Testing Cycles | 1, 3, or 5 cycles | More cycles predict long-term shrinkage behavior |
The International Organization for Standardization provides detailed protocols for shrinkage testing, while the American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists offers complementary methods widely recognized in the U.S. market. Following these standards ensures your test results will be consistent and reliable regardless of where testing occurs.
How to set washing standards for different fabric types?
Setting universal washing standards across all fabric types is a recipe for disaster. The elegant drape of silk requires completely different care than the durability of denim. At Fumao, we develop fabric-specific washing protocols that preserve each material's unique characteristics while ensuring dimensional stability.
Setting washing standards for different fabric types requires understanding each fiber's properties and creating customized care protocols that balance cleaning effectiveness with dimensional preservation. This means establishing different water temperatures, wash cycles, drying methods, and finishing techniques for each fabric category—from delicate silks that need cold water gentle cycles to sturdy cottons that can withstand hotter temperatures and more mechanical action.
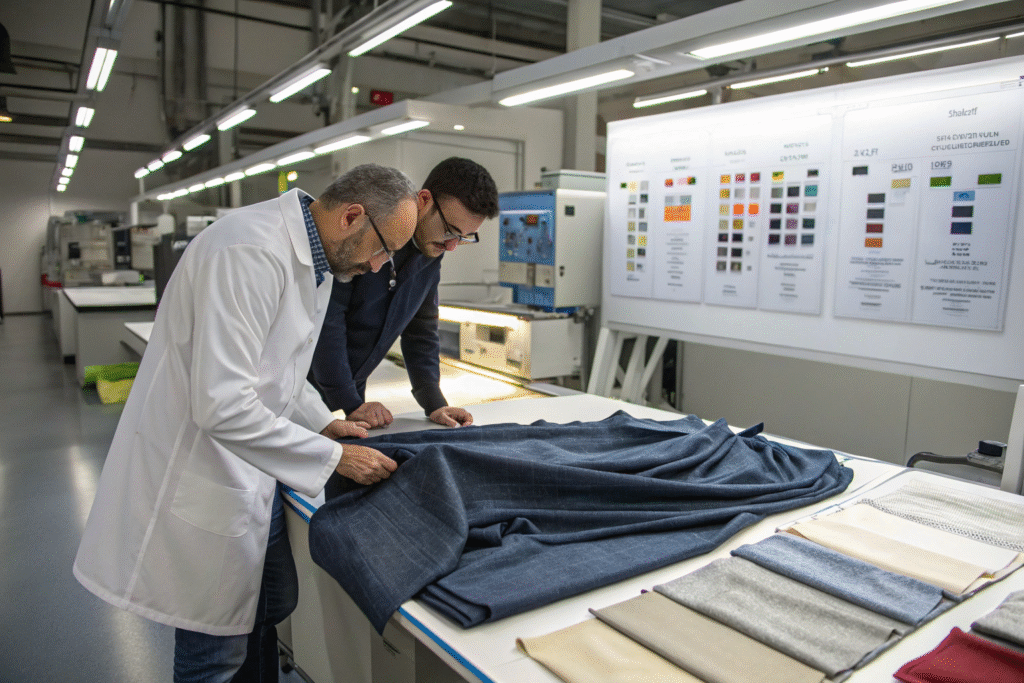

What are the optimal washing standards for natural fibers?
Natural fibers require special consideration as they're most susceptible to shrinkage and damage during laundering. Getting these standards right protects your investment in premium materials.
- Cotton and Linen: These plant-based fibers benefit from pre-shrinking processes like Sanforization or compressive shrinkage before they even reach your cutting table. For washing, we recommend testing at 40°C-60°C (104°F-140°F) as this represents typical consumer washing conditions. Avoid excessive mechanical action which can cause additional shrinkage through fiber friction.
- Wool and Silk: Protein fibers need gentle handling—cold water (below 30°C/86°F), mild detergents, and minimal agitation. For wool, we often recommend testing with both machine washing and hand washing methods to account for different customer care habits. The Woolmark Company provides excellent guidelines for wool care standards that we frequently reference in our testing protocols.
How should you handle synthetic and blended fabrics?
Synthetic fibers and blends present different challenges—while less prone to traditional shrinkage, they can suffer from heat-related distortion and pilling if washed improperly.
- Polyester and Nylon: These synthetics respond well to heat setting during finishing, which stabilizes them against subsequent exposure to heat. Testing should include both warm and hot washes (up to 60°C/140°F) to ensure colorfastness and dimensional stability. Pay special attention to blended fabrics, as the different fiber components may react differently to washing conditions.
- Performance Fabrics: Moisture-wicking, UV-resistant, and elastic textiles require washing standards that preserve their functional properties. We test these fabrics using methods specified by OEKO-TEX® to ensure no loss of functionality after multiple wash cycles, which is particularly important for sportswear and outdoor apparel that must maintain performance throughout its lifespan.
What equipment is needed for shrinkage testing?
You don't need a full-scale laboratory to implement basic shrinkage testing, but understanding the professional equipment used for certification helps you interpret results accurately. When we test fabrics for clients like you, we use specific tools that generate reliable, repeatable data.
The essential equipment for professional shrinkage testing includes standardized washing machines, controlled drying systems, precise measuring instruments, and consistent marking tools. This equipment must be calibrated regularly to ensure accurate results. For basic testing, you can achieve reasonable accuracy with simple tools, but certification requires investment in specialized equipment that follows international standards.
What are the essential tools for basic shrinkage assessment?
Even with limited resources, you can establish a reliable testing process that catches major shrinkage issues before production begins.
- Measuring Tools: Precision rulers, transparent measuring grids, and fabric markers create your foundation. Digital calipers provide more accurate measurements for smaller samples. The key is consistency—always use the same tools and methods for comparable results.
- Washing and Drying Equipment: While standardized machines are ideal, you can use domestic washers and dryers if you document and replicate settings precisely. The critical factors are consistent water temperature, cycle type, and drying method that match your customers' expected care routines.
When should you invest in professional testing equipment?
As your business grows, investing in professional equipment becomes necessary to maintain quality control and meet international standards for your clients.
- Standardized Testing Machines: These include specialized laboratory washers like the James Heal or Wascator models that provide exact control over water volume, temperature, and mechanical action. While expensive, they eliminate variables and produce certification-ready results that major retailers require.
- Environmental Control Systems: Professional labs maintain consistent temperature and humidity (65% ± 2% RH, 20°C ± 2°C) as environmental conditions significantly impact measurement accuracy. Conditioning racks allow fabrics to relax in standard atmospheres before final measurements, following ASTM International guidelines for textile testing.
How to implement shrinkage control in production?
Knowing how to measure shrinkage is pointless unless you can implement effective controls throughout your production process. From our experience serving American clients, the most successful implementations combine technical knowledge with practical production management.
Implementing shrinkage control in production requires establishing checkpoints at raw material intake, during finishing processes, and before final shipment. This systematic approach ensures shrinkage standards are maintained consistently across production batches. The key is creating a culture where everyone from weavers to finishers understands their role in dimensional stability.

What pre-production steps minimize shrinkage issues?
Proactive measures during fabric development and sourcing prevent most shrinkage problems before manufacturing even begins.
- Fiber and Construction Selection: Choose fibers and constructions with known shrinkage characteristics. For example, ring-spun cotton generally shrinks less than open-end spun, and tighter weaves/knits shrink less than looser constructions. Our R&D team can guide you toward stable fabric options for your specific applications.
- Proper Finishing Specifications: Work with your suppliers to implement appropriate shrinkage control finishes. These include compressive shrinkage for wovens, heat-setting for synthetics, and resin treatments for certain fabrics. Our partnership with specialized finishing facilities ensures your fabrics receive the right stabilization treatments for their fiber content.
How can you maintain shrinkage standards during mass production?
Consistent monitoring and clear communication ensure shrinkage control doesn't get compromised during high-volume production runs.
- Batch Testing Protocol: Implement a system where every production batch undergoes shrinkage testing before approval. We maintain a 98% client pass rate by testing three samples from the beginning, middle, and end of each production run, catching variations early.
- Documentation and Communication: Ensure shrinkage data is clearly communicated to all stakeholders. Our QR code tracking system provides real-time access to composition, shrinkage, and colorfastness data, giving you confidence in every meter of fabric you receive. This transparency is particularly valuable for American importers managing complex supply chains across continents.
Conclusion
Controlling fabric shrinkage isn't a mysterious art—it's a science that combines precise measurement, fabric-specific standards, appropriate equipment, and systematic production controls. By understanding both the technical aspects and practical implementation, you can significantly reduce shrinkage-related rejects and protect your brand's reputation for quality. The key is establishing partnerships with suppliers who prioritize dimensional stability throughout their processes.
When you partner with a supplier who understands shrinkage control from fiber to finished fabric, you save time, reduce costs, and deliver better products to your customers. The systematic approach we've outlined represents two decades of refinement in serving global clients who cannot afford surprises with their fabric orders.
If you're tired of shrinkage issues impacting your bottom line, let's discuss how we can implement these practices for your specific product lines. Contact our Business Director Elaine at elaine@fumaoclothing.com to explore how Shanghai Fumao's comprehensive quality control systems can bring consistency and reliability to your fabric sourcing. We'll help you transform shrinkage from a persistent problem into a managed variable.










