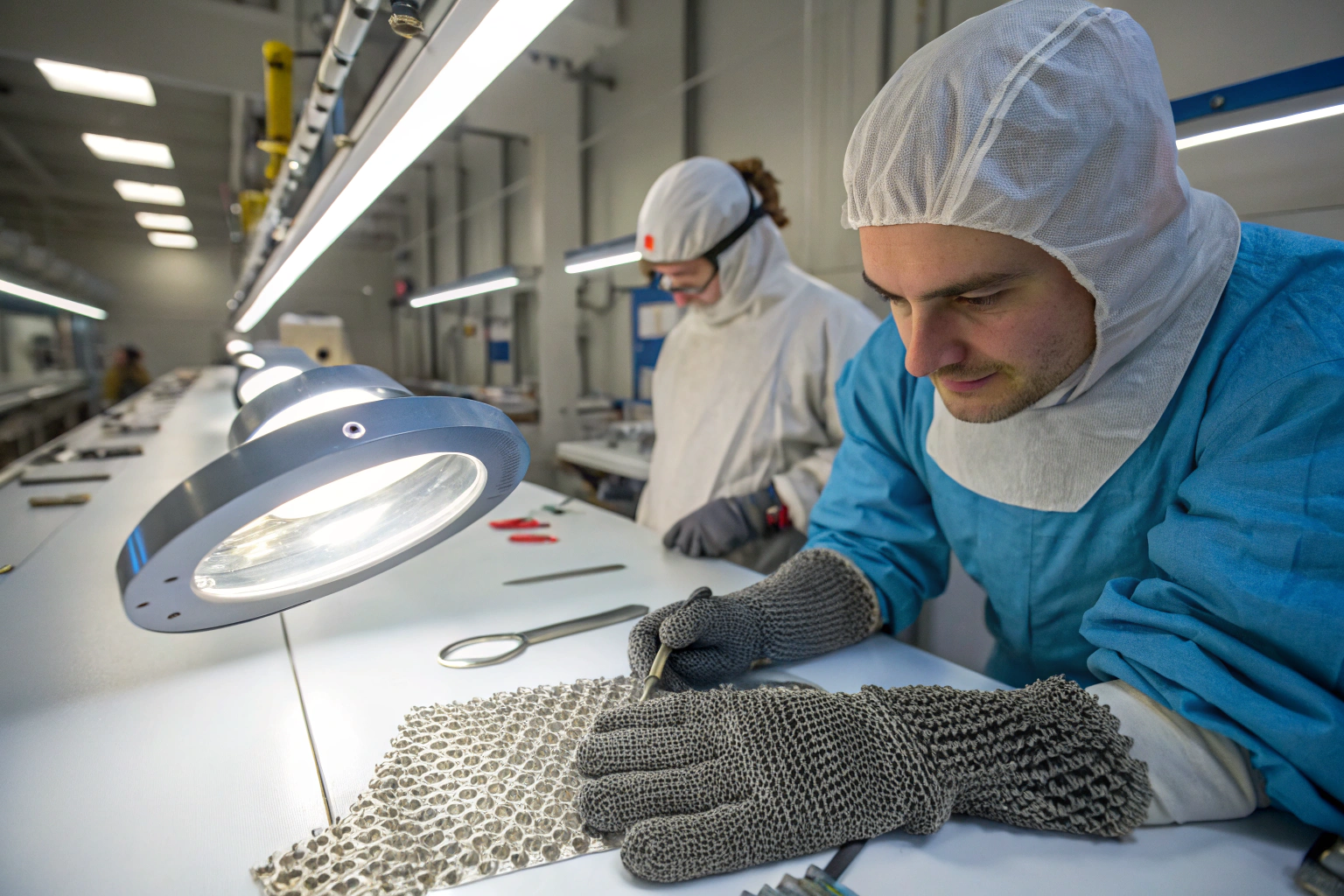
When buyers search for protective textiles like chainmail gloves, aprons, or industrial fabrics, one of the biggest concerns is whether the product can reliably protect against sharp cuts. Many industries—from meat processing to metal fabrication—require clear, standardized proof of safety. Without a reliable benchmark, both manufacturers and buyers risk inconsistent performance and even workplace injuries.
ASTM F2879 provides the globally recognized testing framework for evaluating cut resistance in chainmail materials. It ensures that products meet consistent safety standards, enabling buyers to trust the performance of their protective gear across applications. This standard is now one of the primary references for assessing chainmail textiles, especially in industries where sharp tools are used daily.
Chainmail cut resistance is not just about heavy steel links—it is about how the material behaves under repeated stress, slicing angles, and varying force levels. ASTM F2879 introduces a scientific, repeatable way to measure this, giving manufacturers, buyers, and regulatory bodies a common language. Understanding this helps you, as a buyer, make more informed sourcing decisions.
What Does ASTM F2879 Test for?
ASTM F2879 is designed to simulate realistic cutting conditions that chainmail fabrics face in industrial use. It focuses on ensuring protection against sharp-edged hazards.
In short, ASTM F2879 evaluates how well chainmail prevents penetration and cut-through under applied force.
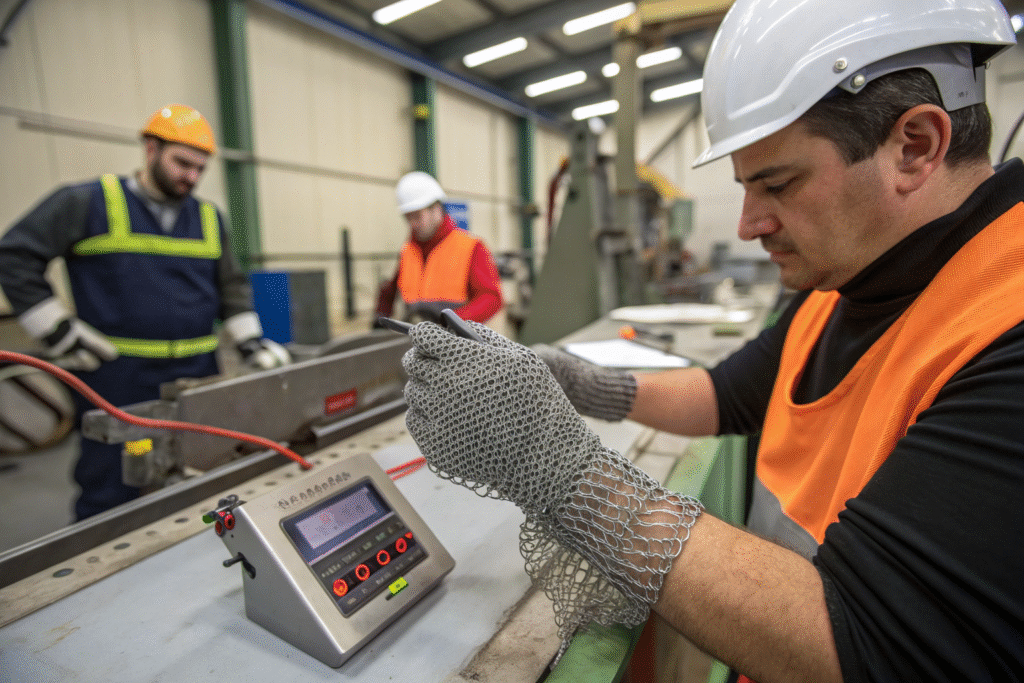

How Does the Testing Process Work?
ASTM F2879 uses a calibrated blade that is applied under controlled force against the chainmail material. The test measures how many cycles or strokes the material can withstand before the blade cuts through. This provides a numerical performance score. You can find additional details directly from ASTM International and references from OSHA safety standards.
This method is critical because chainmail behaves differently compared to woven or knitted fabrics. The interlinked rings deflect and absorb energy, which needs a specific testing approach. ASTM F2879 accounts for this uniqueness.
Why Is This Relevant for Buyers?
If you are sourcing protective gear, ASTM F2879 certification guarantees that the chainmail meets internationally accepted performance requirements. This reduces procurement risks and ensures compliance with workplace safety laws. Buyers can also compare suppliers fairly since the testing eliminates guesswork. For example, meat processing plants in the U.S. require gloves and aprons meeting such standards, ensuring reduced injury rates compared to uncertified gear.
How Does ASTM F2879 Compare to Other Cut Resistance Standards?
Chainmail is not tested the same way as textiles like Kevlar or Dyneema. Understanding how ASTM F2879 differs from other standards is essential.
Unlike EN 388 or ISO 13997, ASTM F2879 is designed specifically for chainmail and puncture-prone fabrics.
What Makes ASTM F2879 Unique?
EN 388 (used in Europe) tests gloves for abrasion, cut, tear, and puncture resistance, but it is optimized for woven and knit fabrics. ASTM F2879 fills the gap for chainmail, which performs differently. ISO 13997 measures cut resistance using straight blade force, but it may not reflect how chainmail distributes force. More information can be explored at BSI Group standards and ANSI cut protection guidelines.
By focusing on linked-ring structures, ASTM F2879 gives buyers a more realistic view of actual performance in chainmail applications.
How Should Buyers Use This Knowledge?
If you are comparing suppliers across Europe and the U.S., you may find one offering EN 388 compliance and another ASTM F2879. Buyers should request the specific test method and ask for detailed test reports. This helps avoid confusion and ensures the chainmail is truly fit for its purpose.
Which Industries Rely Most on ASTM F2879?
Chainmail is widely used where sharp cutting tools are involved daily. Knowing which sectors rely on ASTM F2879 helps buyers understand its importance.
The biggest users include meat and poultry processing, seafood handling, metalworking, and security applications.
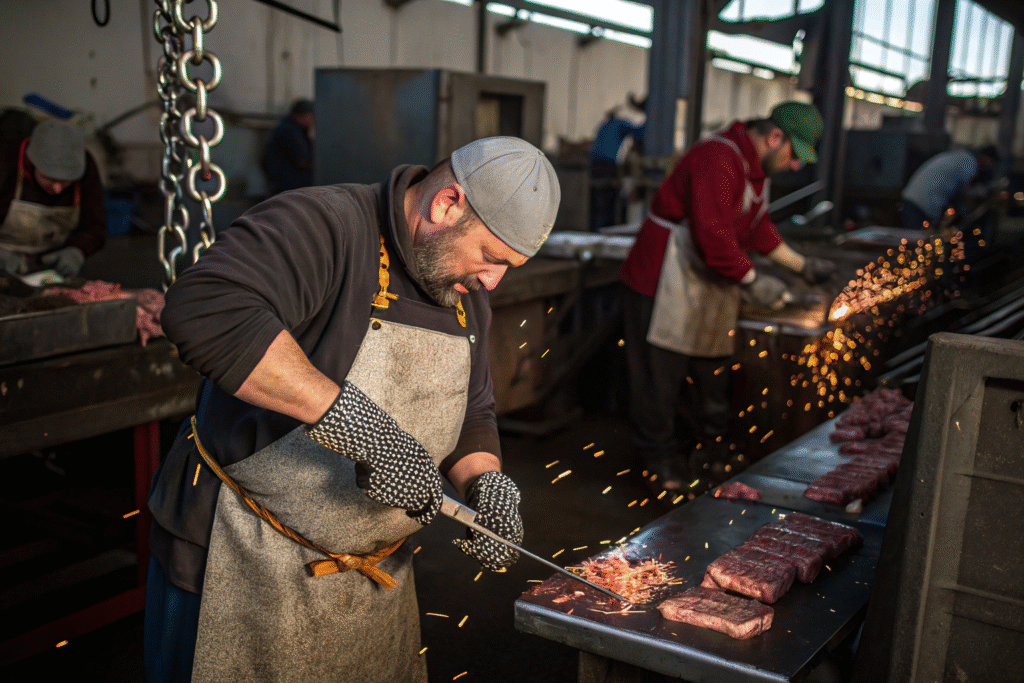

Why Is It Important in Food Processing?
Meat and poultry plants face some of the highest risks of cut injuries. Workers handling knives need chainmail aprons and gloves tested under ASTM F2879 to ensure reliable protection. The U.S. Department of Agriculture and NIOSH highlight cut-resistant gear as essential to reducing injuries. This ensures that both safety and compliance are met.
How About Industrial and Security Applications?
Metalworkers, glass handlers, and even some law enforcement units rely on chainmail protection. ASTM F2879 ensures that the gear can withstand real-world hazards, not just laboratory conditions. Buyers in these industries should always prioritize ASTM F2879-certified gear to align with both OSHA and international safety protocols. More background can be found at SAFETY+HEALTH magazine.
What Should Buyers Look for When Sourcing ASTM F2879 Chainmail?
As a buyer, knowing the certification is important, but there are other factors that influence your final choice.
ASTM F2879 is a baseline—but quality control, supplier reliability, and after-sales service are equally critical.
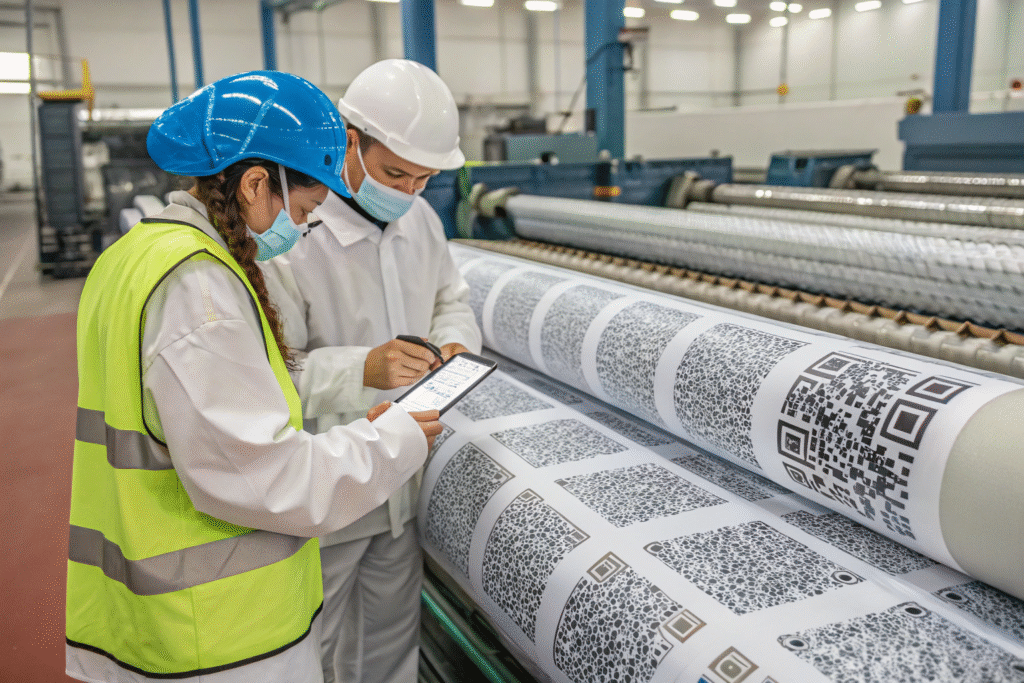

What Are the Key Procurement Questions?
Buyers should ask suppliers for complete test reports, batch inspection details, and sample validation. They should also check if the supplier works with accredited labs such as SGS or Intertek. For best practices, review SGS textile testing services and Intertek assurance testing. These certifications add another layer of trust beyond ASTM F2879.
How Can Buyers Ensure Long-Term Reliability?
Suppliers that integrate ASTM F2879 testing into their full quality assurance system tend to deliver more consistent performance. Buyers should look for QR code tracking systems, lot traceability, and strong after-sales support. These are signs that the supplier is not just chasing compliance but is invested in product safety and durability.
Conclusion
ASTM F2879 is not just another testing standard. It is the backbone of safety assurance for chainmail cut resistance. It allows manufacturers to prove compliance, and it gives buyers the confidence to source protective gear without second-guessing performance. For industries where sharp hazards are part of everyday operations, this standard is a non-negotiable requirement.
If you are looking to co-develop or source fabrics that meet ASTM standards—including chainmail and other technical textiles—our team at Shanghai Fumao is ready to support you. You can contact our Business Director, Elaine, at elaine@fumaoclothing.com to discuss your fabric needs and custom development projects.










