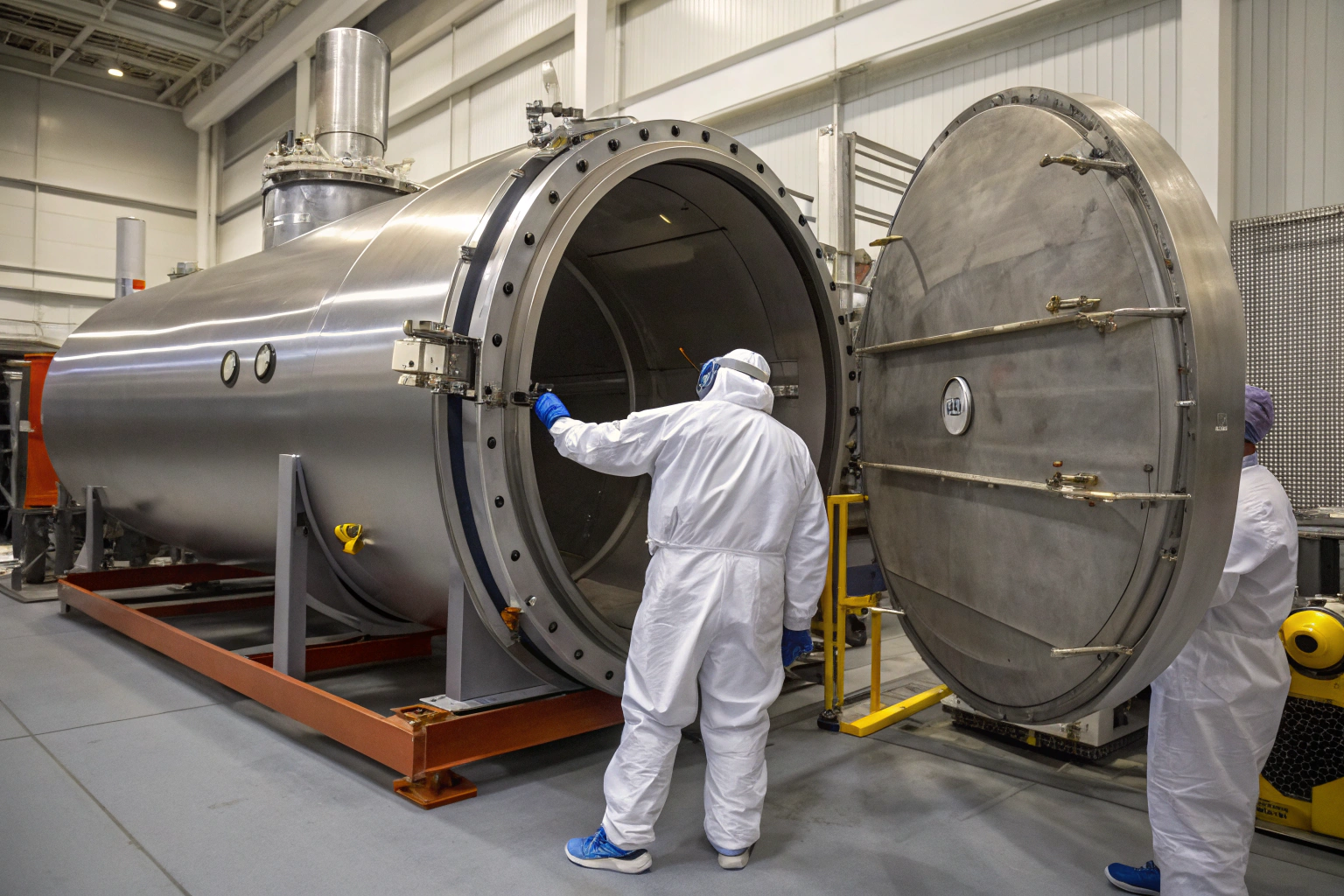
When working with vacuum chambers, every detail matters. Engineers, scientists, and manufacturers often struggle to identify fabrics that can perform under such demanding conditions. The wrong choice can lead to system contamination, material failure, or even the shutdown of critical experiments. This challenge raises an important question—what are the fabrics that can truly survive and perform inside vacuum chambers?
The best fabrics for vacuum chamber applications are fiberglass, Kevlar and aramid textiles, PTFE-coated fabrics, and polyimide-based fabrics. These options stand out because they combine low outgassing, excellent temperature resistance, and reliable structural performance under vacuum conditions.
Finding the right material means balancing safety, performance, and cost. By understanding the strengths of each option, you can make informed decisions for aerospace, semiconductor, research, and industrial applications.
Fiberglass Fabrics for High-Temperature Applications
Fiberglass fabrics are widely chosen for vacuum chambers because of their ability to withstand extreme heat and stress. They provide strength, insulation, and durability, making them reliable in conditions that exceed 500°C.
Fiberglass is one of the most reliable fabrics for vacuum chambers because it combines thermal stability with low outgassing and adaptability through coatings like PTFE or silicone.
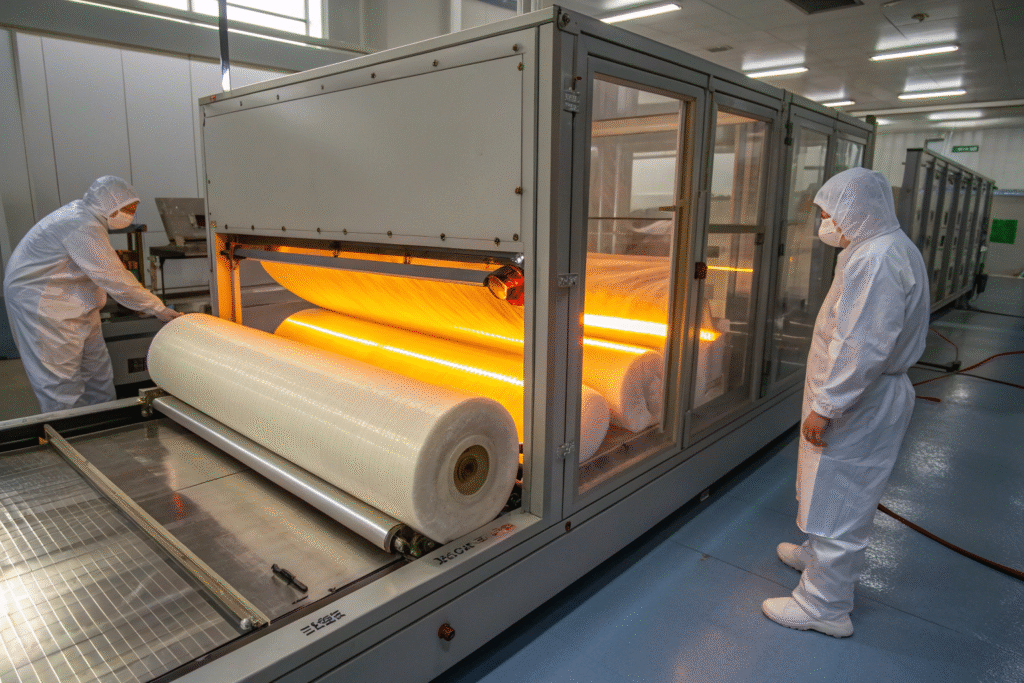

Why is fiberglass a strong choice for aerospace vacuum use?
Fiberglass remains stable under severe thermal and mechanical stress. This is why NASA and other aerospace agencies rely on fiberglass composites in vacuum testing. It shows very low outgassing under ASTM E595 testing, which prevents contamination of sensitive instruments.
Can fiberglass be customized for laboratory chambers?
Yes. Fiberglass fabrics can be laminated with Kapton polyimide films or adjusted in weave density to fit specific chambers. This gives researchers flexibility in balancing strength with insulation needs for different applications.
Kevlar and Aramid Textiles for Strength
Kevlar and other aramid textiles are preferred when strength and stability are required. They resist tearing, vibration, and stress, making them ideal for chambers where parts are exposed to strong movement or repeated tests.
Kevlar fabrics provide lightweight reinforcement and high tensile strength, ensuring reliable performance without contamination in vacuum conditions.
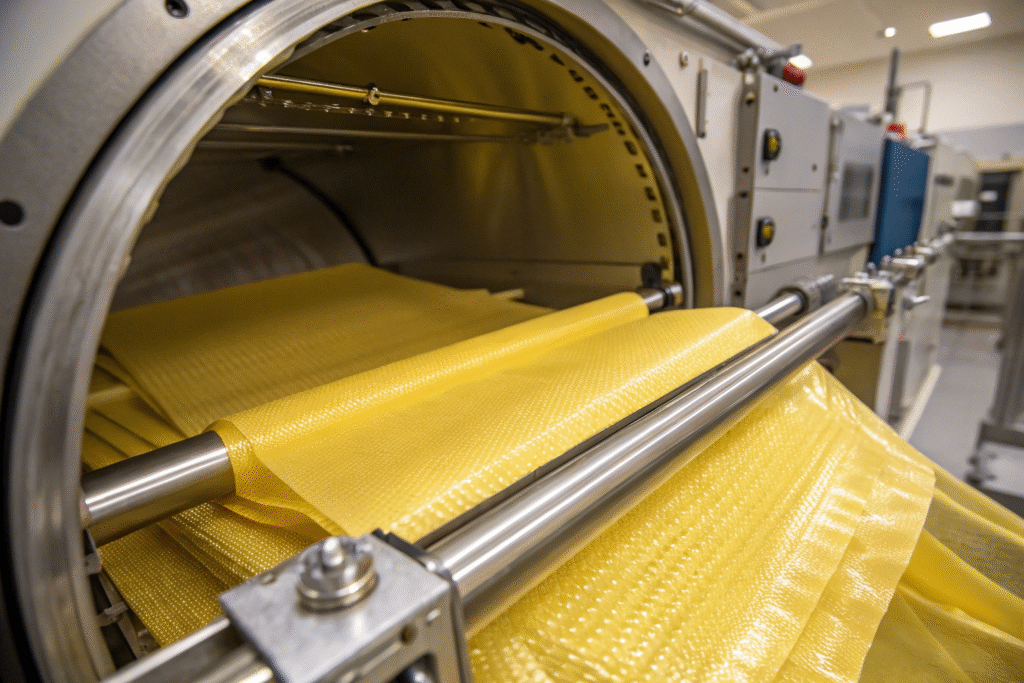

How does Kevlar reduce vibration in vacuum systems?
Kevlar is lightweight yet incredibly strong. It reduces unwanted vibration in sensitive semiconductor alignment systems. This makes it essential for equipment that demands precision under vacuum stress.
Is Kevlar compatible with cleaning and plasma treatments?
Yes. Kevlar holds up well during chamber cleaning processes. To improve its resistance against UV and plasma degradation, Kevlar fabrics are often coated with epoxy resins or polyurethane. This extends their life and stability inside vacuum labs.
PTFE-Coated Fabrics for Chemical Protection
PTFE-coated fabrics are known for their non-stick surface, chemical resistance, and flexibility. By coating fiberglass or aramid fabrics, PTFE combines structural strength with unique protective features.
PTFE-coated fabrics are especially effective when vacuum chambers involve reactive chemicals, solvents, or plasma environments.
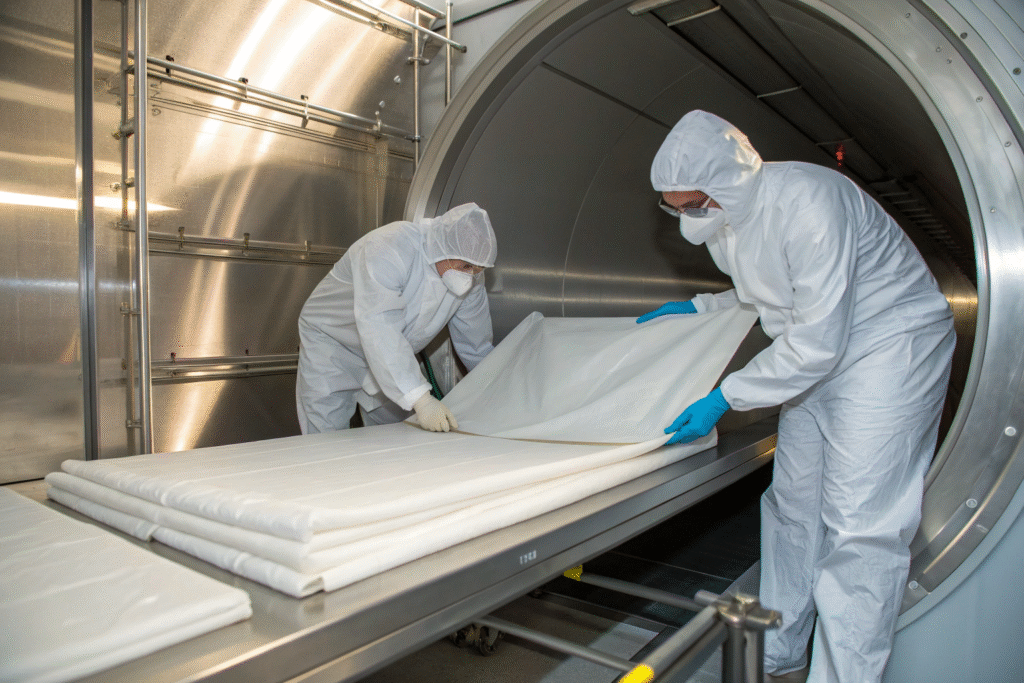

Why is PTFE important for semiconductor vacuum chambers?
Semiconductor production requires clean and resistant surfaces. PTFE coatings prevent chemical buildup and meet ISO cleanroom standards. This makes them vital for vacuum chambers used in etching or plasma cleaning.
Can PTFE fabrics handle cryogenic vacuum environments?
Yes. PTFE keeps flexibility even at extremely low temperatures. It is often used in cryopumps where sealing must remain intact under freezing conditions.
Polyimide-Based Fabrics for Extreme Environments
Polyimide-based fabrics, such as Kapton®, are considered the top-tier choice for extreme vacuum use. They retain dielectric and mechanical properties even at high heat and show some of the lowest outgassing rates.
Polyimide fabrics are unmatched in environments where radiation, high heat, and electrical insulation must all be managed simultaneously.
Why is polyimide favored for space vacuum chambers?
Polyimide is radiation-resistant and stable in outer space. It is commonly used in satellite insulation blankets, ensuring long-term survival of instruments in radiation-heavy conditions.
Can polyimide be combined with metals for more protection?
Yes. Polyimide fabrics are often coated with aluminum or gold to create multilayer insulation, a method applied in aerospace thermal systems. This combination enhances heat reflection and extends the life of materials under harsh vacuum conditions.
Conclusion
Vacuum chambers demand fabrics that can handle extreme stress. Fiberglass delivers insulation and strength, Kevlar ensures structural support, PTFE resists chemical attack, and polyimide excels in space-level challenges.
At Shanghai Fumao, we supply advanced technical fabrics customized for vacuum chambers and related industries. Our portfolio includes fiberglass, Kevlar, PTFE-coated, and polyimide fabrics, tested for low outgassing and global compliance. To discuss your custom needs, please connect with our Business Director Elaine at elaine@fumaoclothing.com.










